Graph Representation Learning Network via Adaptive Sampling
Paper and Code
Jun 08, 2020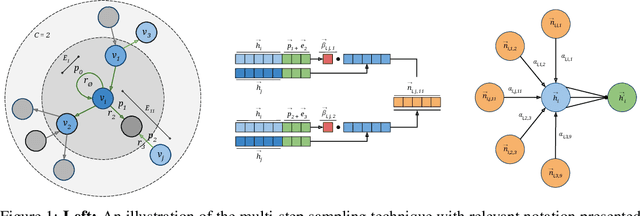
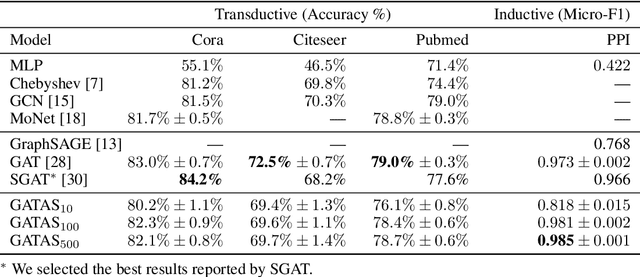
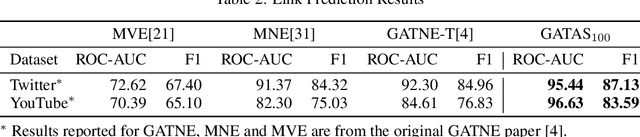
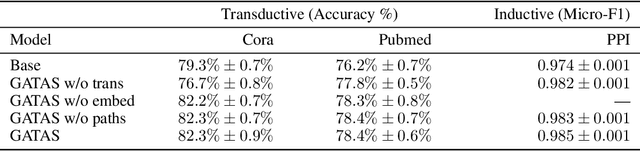
Graph Attention Network (GAT) and GraphSAGE are neural network architectures that operate on graph-structured data and have been widely studied for link prediction and node classification. One challenge raised by GraphSAGE is how to smartly combine neighbour features based on graph structure. GAT handles this problem through attention, however the challenge with GAT is its scalability over large and dense graphs. In this work, we proposed a new architecture to address these issues that is more efficient and is capable of incorporating different edge type information. It generates node representations by attending to neighbours sampled from weighted multi-step transition probabilities. We conduct experiments on both transductive and inductive settings. Experiments achieved comparable or better results on several graph benchmarks, including the Cora, Citeseer, Pubmed, PPI, Twitter, and YouTube datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge