Graph Neural Network-enabled Terahertz-based Flow-guided Nanoscale Localization
Paper and Code
Jul 09, 2023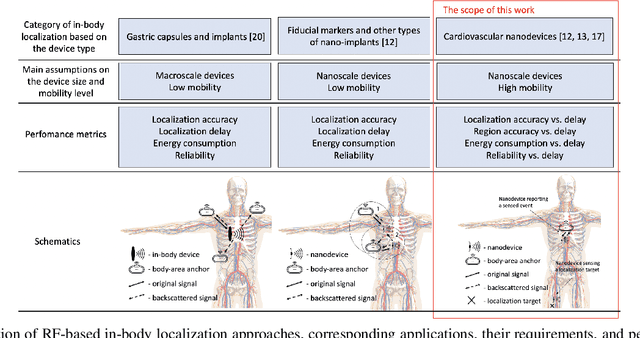
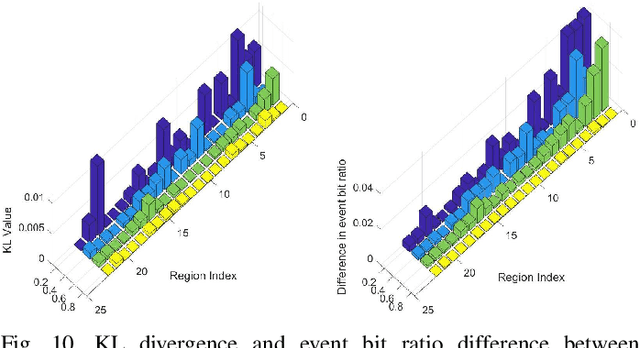
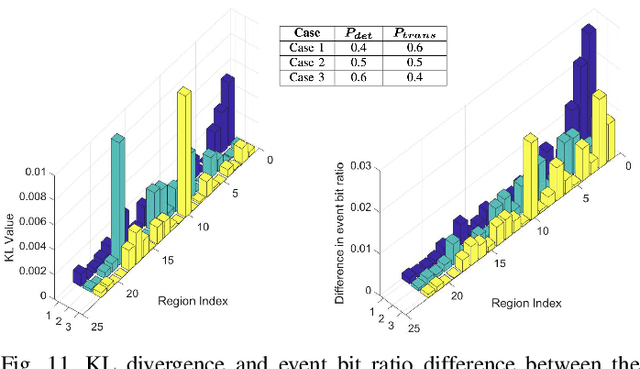
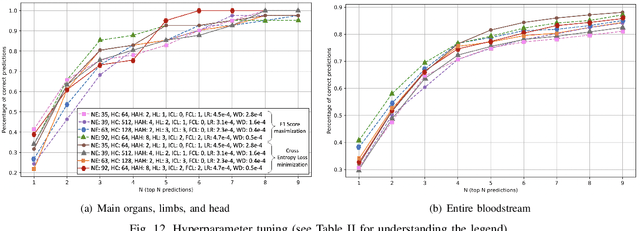
Scientific advancements in nanotechnology and advanced materials are paving the way toward nanoscale devices for in-body precision medicine; comprising integrated sensing, computing, communication, data and energy storage capabilities. In the human cardiovascular system, such devices are envisioned to be passively flowing and continuously sensing for detecting events of diagnostic interest. The diagnostic value of detecting such events can be enhanced by assigning to them their physical locations (e.g., body region), which is the main proposition of flow-guided localization. Current flow-guided localization approaches suffer from low localization accuracy and they are by-design unable to localize events within the entire cardiovascular system. Toward addressing this issue, we propose the utilization of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) for this purpose, and demonstrate localization accuracy and coverage enhancements of our proposal over the existing State of the Art (SotA) approaches. Based on our evaluation, we provide several design guidelines for GNN-enabled flow-guided localization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge