Graph Kernel Attention Transformers
Paper and Code
Jul 16, 2021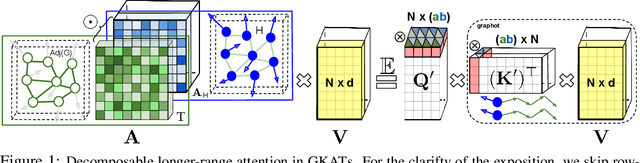
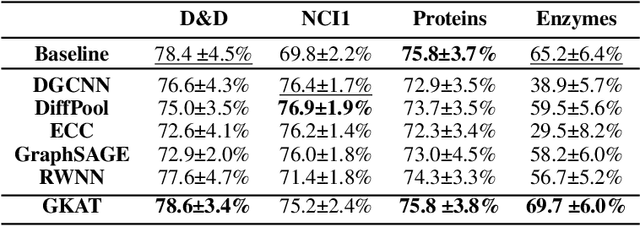
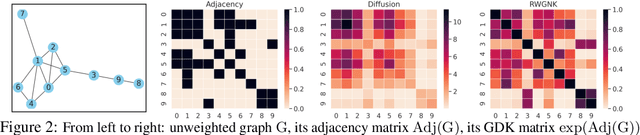
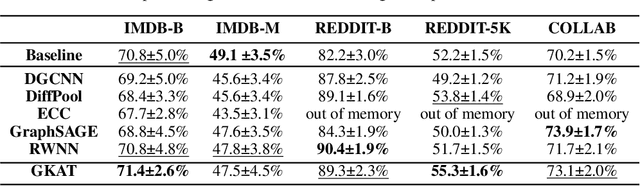
We introduce a new class of graph neural networks (GNNs), by combining several concepts that were so far studied independently - graph kernels, attention-based networks with structural priors and more recently, efficient Transformers architectures applying small memory footprint implicit attention methods via low rank decomposition techniques. The goal of the paper is twofold. Proposed by us Graph Kernel Attention Transformers (or GKATs) are much more expressive than SOTA GNNs as capable of modeling longer-range dependencies within a single layer. Consequently, they can use more shallow architecture design. Furthermore, GKAT attention layers scale linearly rather than quadratically in the number of nodes of the input graphs, even when those graphs are dense, requiring less compute than their regular graph attention counterparts. They achieve it by applying new classes of graph kernels admitting random feature map decomposition via random walks on graphs. As a byproduct of the introduced techniques, we obtain a new class of learnable graph sketches, called graphots, compactly encoding topological graph properties as well as nodes' features. We conducted exhaustive empirical comparison of our method with nine different GNN classes on tasks ranging from motif detection through social network classification to bioinformatics challenges, showing consistent gains coming from GKATs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge