Graph-Based Recommendation System
Paper and Code
Jul 31, 2018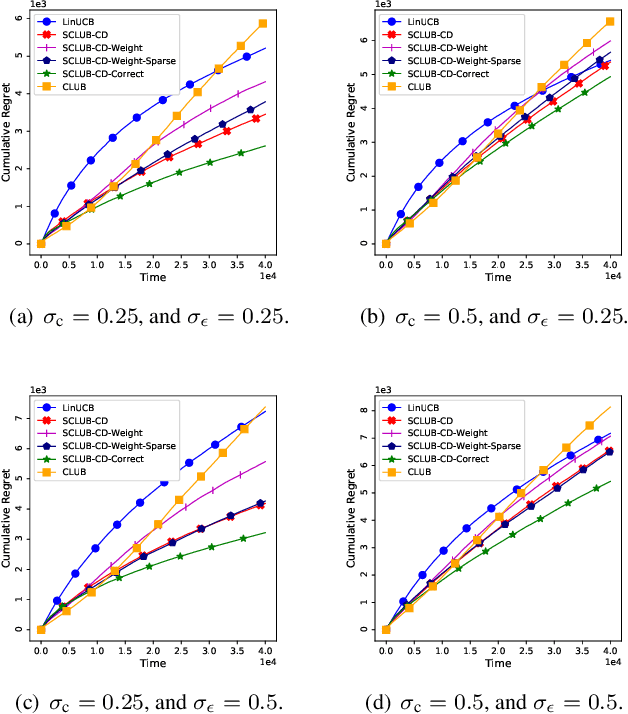
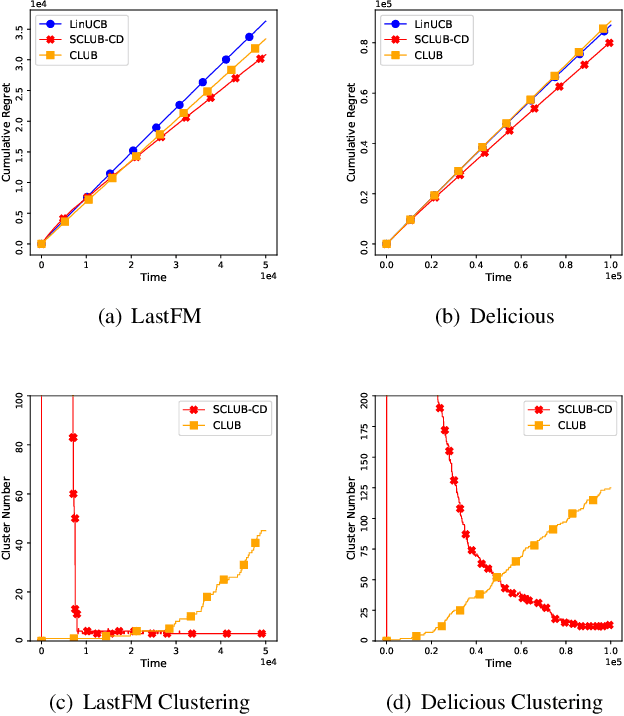
In this work, we study recommendation systems modelled as contextual multi-armed bandit (MAB) problems. We propose a graph-based recommendation system that learns and exploits the geometry of the user space to create meaningful clusters in the user domain. This reduces the dimensionality of the recommendation problem while preserving the accuracy of MAB. We then study the effect of graph sparsity and clusters size on the MAB performance and provide exhaustive simulation results both in synthetic and in real-case datasets. Simulation results show improvements with respect to state-of-the-art MAB algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge