Granular Ball Twin Support Vector Machine
Paper and Code
Oct 07, 2024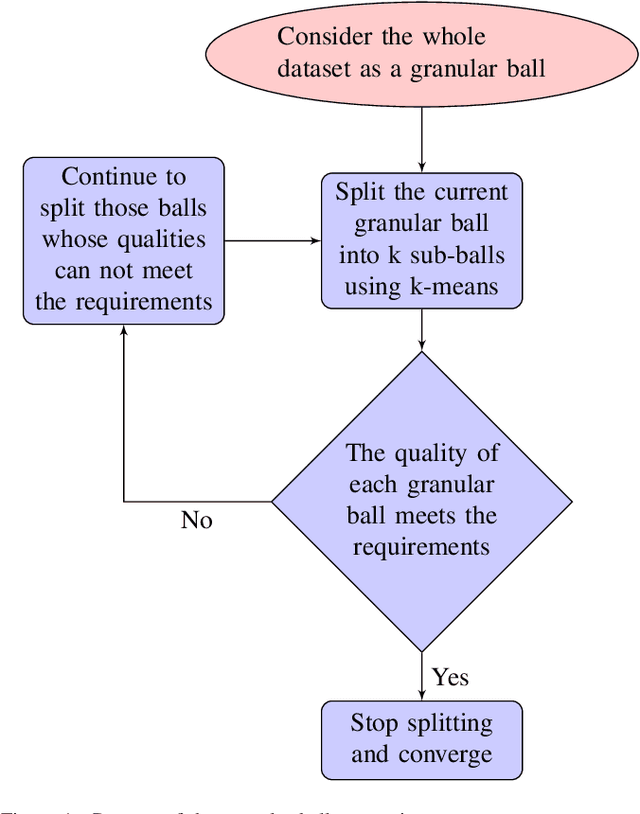
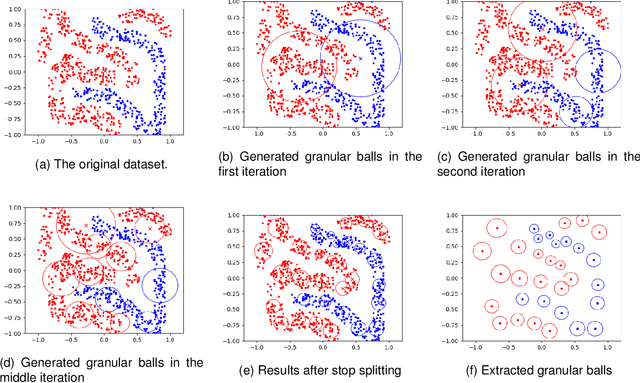
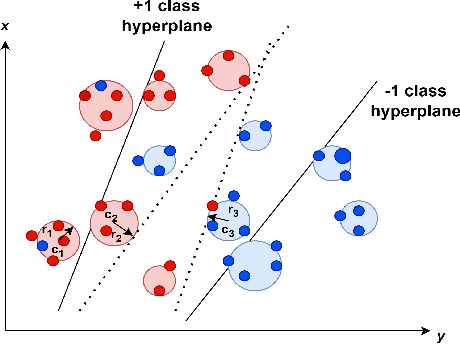
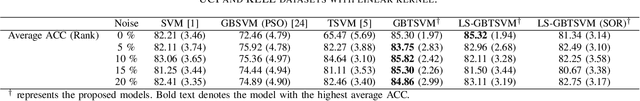
On Efficient and Scalable Computation of the Nonparametric Maximum Likelihood Estimator in Mixture ModelsTwin support vector machine (TSVM) is an emerging machine learning model with versatile applicability in classification and regression endeavors. Nevertheless, TSVM confronts noteworthy challenges: $(i)$ the imperative demand for matrix inversions presents formidable obstacles to its efficiency and applicability on large-scale datasets; $(ii)$ the omission of the structural risk minimization (SRM) principle in its primal formulation heightens the vulnerability to overfitting risks; and $(iii)$ the TSVM exhibits a high susceptibility to noise and outliers, and also demonstrates instability when subjected to resampling. In view of the aforementioned challenges, we propose the granular ball twin support vector machine (GBTSVM). GBTSVM takes granular balls, rather than individual data points, as inputs to construct a classifier. These granular balls, characterized by their coarser granularity, exhibit robustness to resampling and reduced susceptibility to the impact of noise and outliers. We further propose a novel large-scale granular ball twin support vector machine (LS-GBTSVM). LS-GBTSVM's optimization formulation ensures two critical facets: $(i)$ it eliminates the need for matrix inversions, streamlining the LS-GBTSVM's computational efficiency, and $(ii)$ it incorporates the SRM principle through the incorporation of regularization terms, effectively addressing the issue of overfitting. The proposed LS-GBTSVM exemplifies efficiency, scalability for large datasets, and robustness against noise and outliers. We conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the GBTSVM and LS-GBTSVM models on benchmark datasets from UCI, KEEL, and NDC datasets. Our experimental findings and statistical analyses affirm the superior generalization prowess of the proposed GBTSVM and LS-GBTSVM models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge