Gradient-free training of autoencoders for non-differentiable communication channels
Paper and Code
Dec 21, 2020
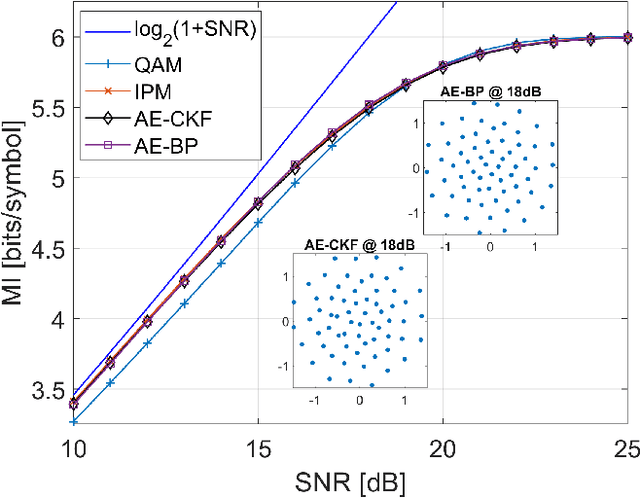
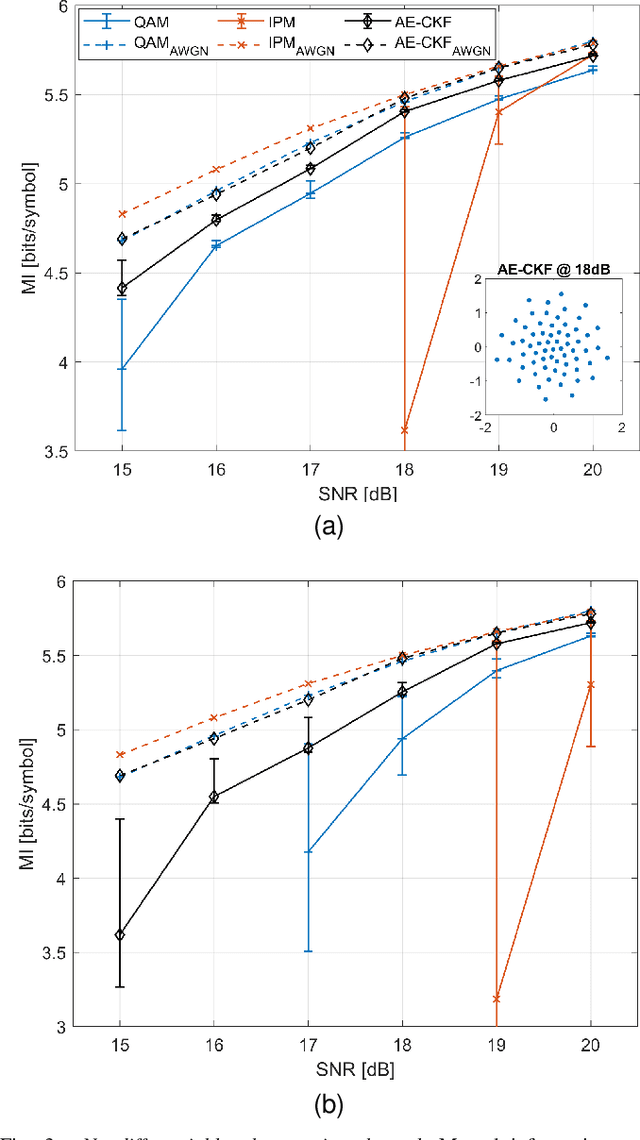
Training of autoencoders using the backpropagation algorithm is challenging for non-differential channel models or in an experimental environment where gradients cannot be computed. In this paper, we study a gradient-free training method based on the cubature Kalman filter. To numerically investigate the method, the autoencoder is employed to perform geometric constellation shaping on a non-differentiable communication channel that includes: laser phase noise, additive white Gaussian noise and blind phase search-based phase noise compensation. Our results indicate that the autoencoder can be successfully optimized using the proposed training method. We also show that the learned constellations are more robust to residual phase noise with respect to standard constellation schemes such as Quadratude Amplitude Modulation and Iterative Polar Modulation for the considered conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge