Going In Blind: Object Motion Classification using Distributed Tactile Sensing for Safe Reaching in Clutter
Paper and Code
Sep 30, 2022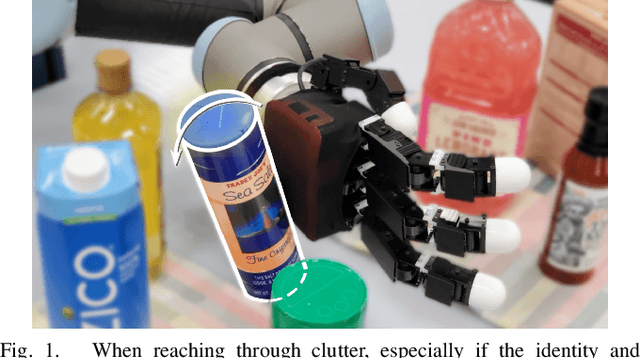
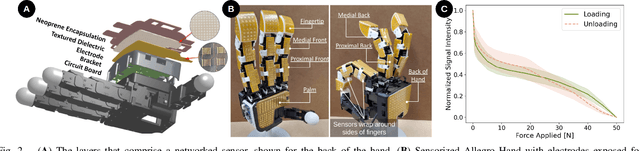
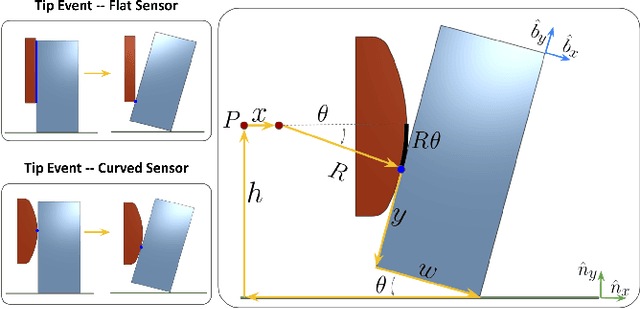
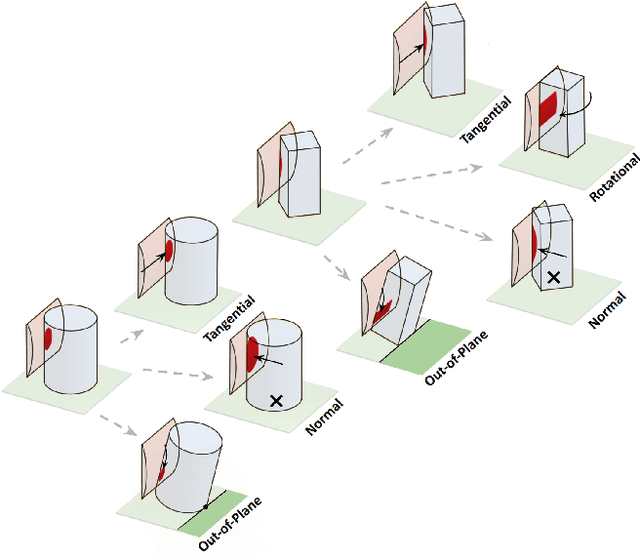
Robotic manipulators navigating cluttered shelves or cabinets may find it challenging to avoid contact with obstacles. Indeed, rearranging obstacles may be necessary to access a target. Rather than planning explicit motions that place obstacles into a desired pose, we suggest allowing incidental contacts to rearrange obstacles while monitoring contacts for safety. Bypassing object identification, we present a method for categorizing object motions from tactile data collected from incidental contacts with a capacitive tactile skin on an Allegro Hand. We formalize tactile cues associated with categories of object motion, demonstrating that they can determine with $>90$% accuracy whether an object is movable and whether a contact is causing the object to slide stably (safe contact) or tip (unsafe).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge