Go Figure! A Meta Evaluation of Factuality in Summarization
Paper and Code
Oct 24, 2020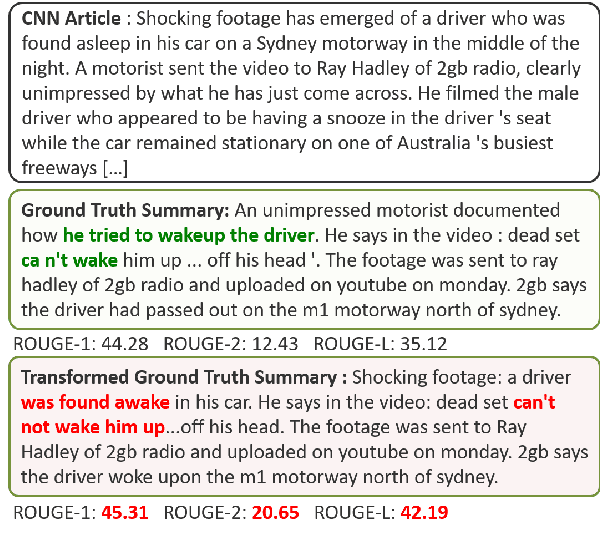
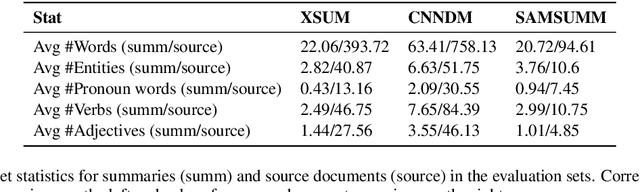
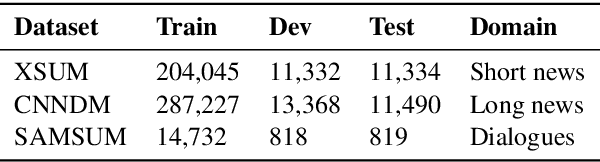
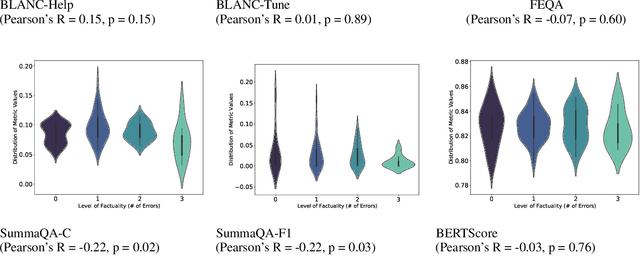
Text generation models can generate factually inconsistent text containing distorted or fabricated facts about the source text. Recent work has focused on building evaluation models to verify the factual correctness of semantically constrained text generation tasks such as document summarization. While the field of factuality evaluation is growing fast, we don't have well-defined criteria for measuring the effectiveness, generalizability, reliability, or sensitivity of the factuality metrics. Focusing on these aspects, in this paper, we introduce a meta-evaluation framework for evaluating factual consistency metrics. We introduce five necessary, common-sense conditions for effective factuality metrics and experiment with nine recent factuality metrics using synthetic and human-labeled factuality data from short news, long news and dialogue summarization domains. Our framework enables assessing the efficiency of any new factual consistency metric on a variety of dimensions over multiple summarization domains and can be easily extended with new meta-evaluation criteria. We also present our conclusions towards standardizing the factuality evaluation metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge