Global Rewards in Restless Multi-Armed Bandits
Paper and Code
Jun 02, 2024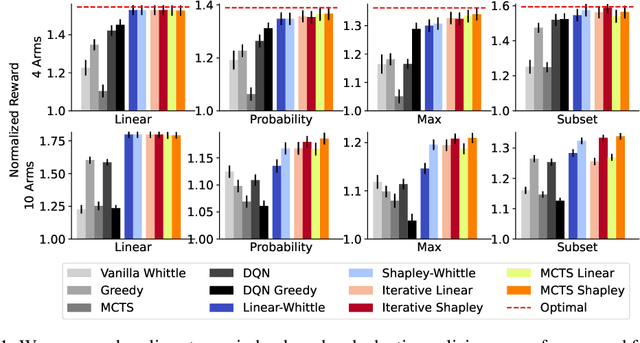
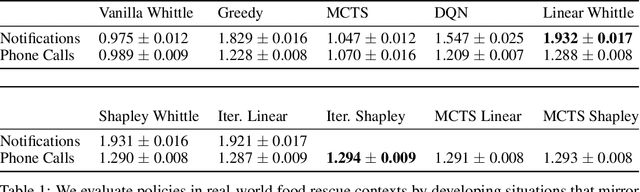
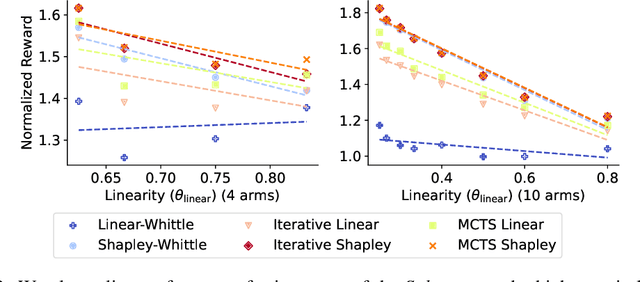
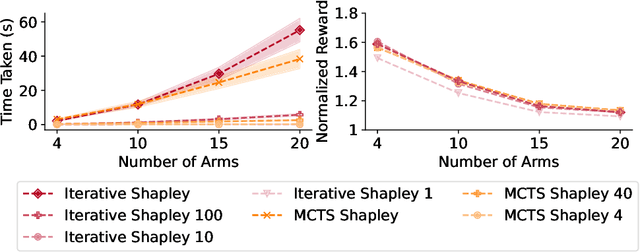
Restless multi-armed bandits (RMAB) extend multi-armed bandits so pulling an arm impacts future states. Despite the success of RMABs, a key limiting assumption is the separability of rewards into a sum across arms. We address this deficiency by proposing restless-multi-armed bandit with global rewards (RMAB-G), a generalization of RMABs to global non-separable rewards. To solve RMAB-G, we develop the Linear- and Shapley-Whittle indices, which extend Whittle indices from RMABs to RMAB-Gs. We prove approximation bounds but also point out how these indices could fail when reward functions are highly non-linear. To overcome this, we propose two sets of adaptive policies: the first computes indices iteratively, and the second combines indices with Monte-Carlo Tree Search (MCTS). Empirically, we demonstrate that our proposed policies outperform baselines and index-based policies with synthetic data and real-world data from food rescue.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge