GLADIS: A General and Large Acronym Disambiguation Benchmark
Paper and Code
Feb 03, 2023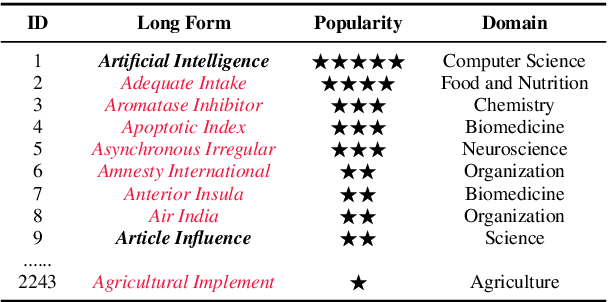
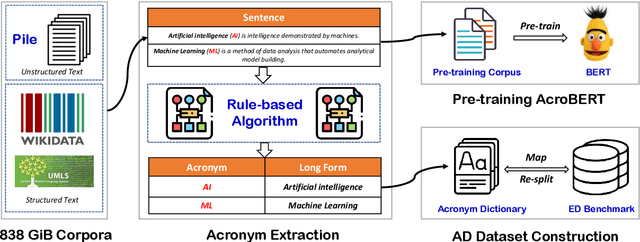
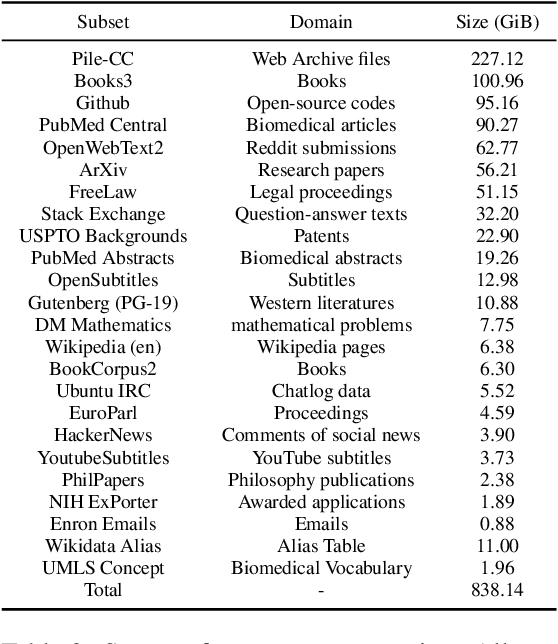

Acronym Disambiguation (AD) is crucial for natural language understanding on various sources, including biomedical reports, scientific papers, and search engine queries. However, existing acronym disambiguation benchmarks and tools are limited to specific domains, and the size of prior benchmarks is rather small. To accelerate the research on acronym disambiguation, we construct a new benchmark named GLADIS with three components: (1) a much larger acronym dictionary with 1.5M acronyms and 6.4M long forms; (2) a pre-training corpus with 160 million sentences; (3) three datasets that cover the general, scientific, and biomedical domains. We then pre-train a language model, \emph{AcroBERT}, on our constructed corpus for general acronym disambiguation, and show the challenges and values of our new benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge