Giving BERT a Calculator: Finding Operations and Arguments with Reading Comprehension
Paper and Code
Sep 12, 2019
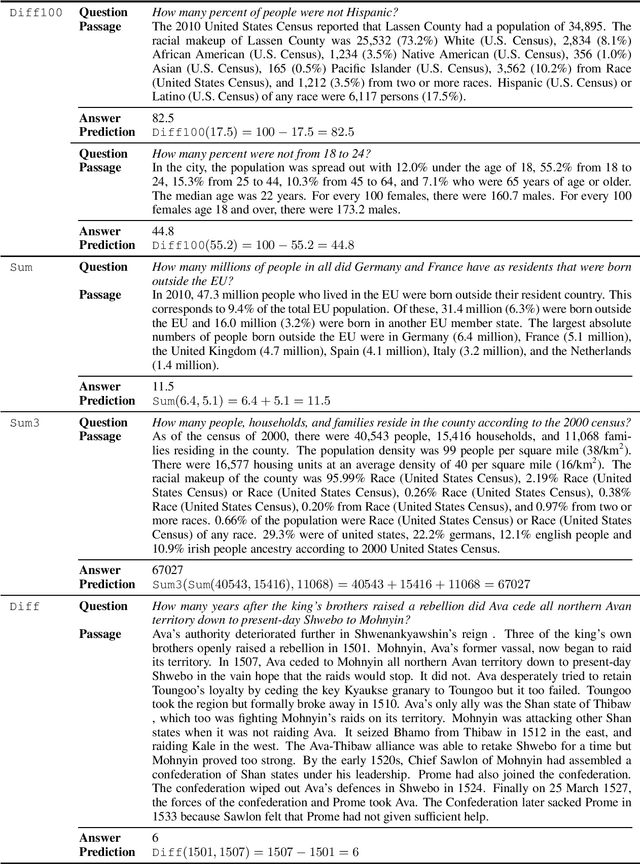
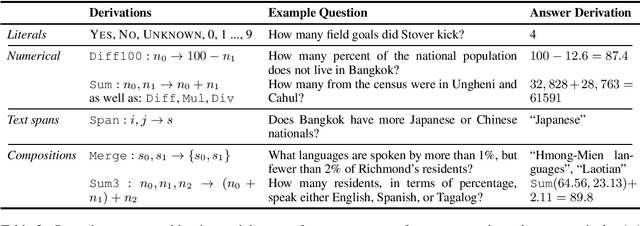

Reading comprehension models have been successfully applied to extractive text answers, but it is unclear how best to generalize these models to abstractive numerical answers. We enable a BERT-based reading comprehension model to perform lightweight numerical reasoning. We augment the model with a predefined set of executable 'programs' which encompass simple arithmetic as well as extraction. Rather than having to learn to manipulate numbers directly, the model can pick a program and execute it. On the recent Discrete Reasoning Over Passages (DROP) dataset, designed to challenge reading comprehension models, we show a 33% absolute improvement by adding shallow programs. The model can learn to predict new operations when appropriate in a math word problem setting (Roy and Roth, 2015) with very few training examples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge