Geo-referencing Place from Everyday Natural Language Descriptions
Paper and Code
Oct 09, 2017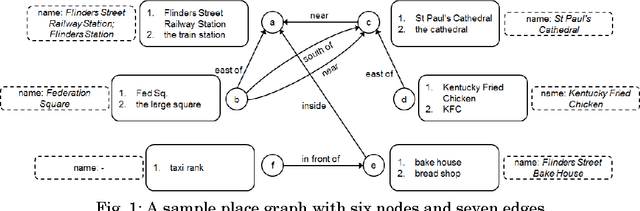
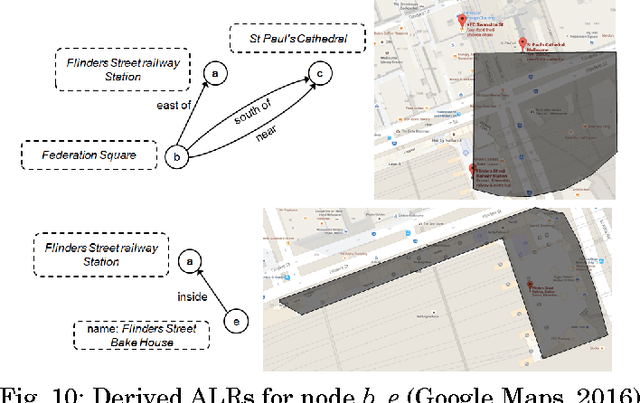
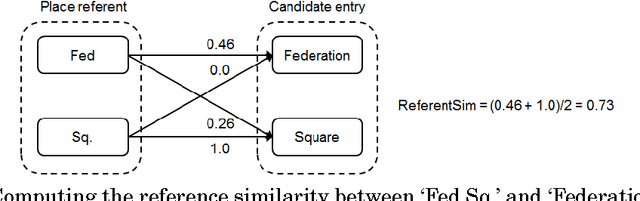
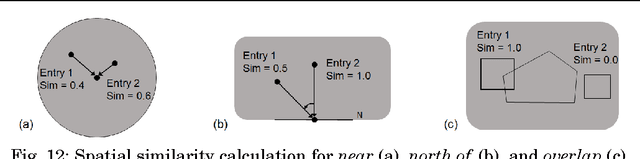
Natural language place descriptions in everyday communication provide a rich source of spatial knowledge about places. An important step to utilize such knowledge in information systems is geo-referencing all the places referred to in these descriptions. Current techniques for geo-referencing places from text documents are using place name recognition and disambiguation; however, place descriptions often contain place references that are not known by gazetteers, or that are expressed in other, more flexible ways. Hence, the approach for geo-referencing presented in this paper starts from a place graph that contains the place references as well as spatial relationships extracted from place descriptions. Spatial relationships are used to constrain the locations of places and allow the later best-matching process for geo-referencing. The novel geo-referencing process results in higher precision and recall compared to state-of-art toponym resolution approaches on several tested place description datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge