Generating Positive Bounding Boxes for Balanced Training of Object Detectors
Paper and Code
Sep 21, 2019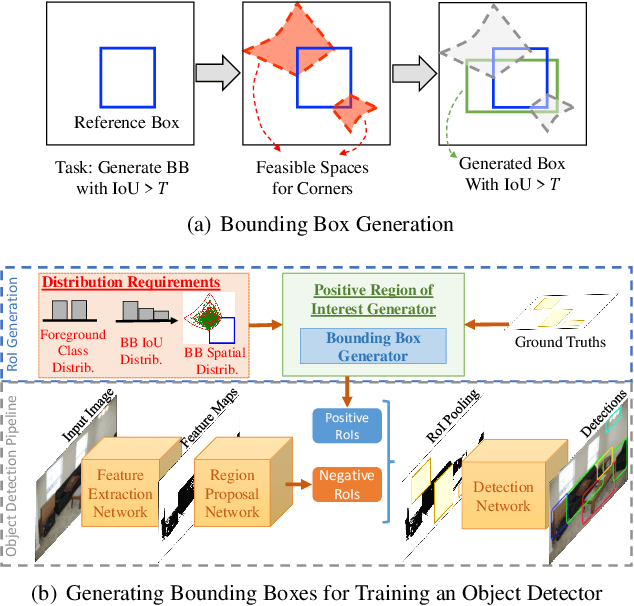
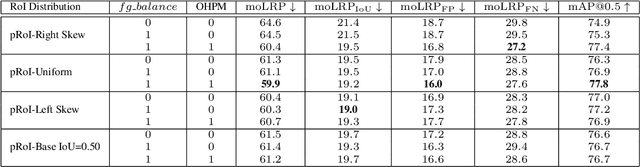
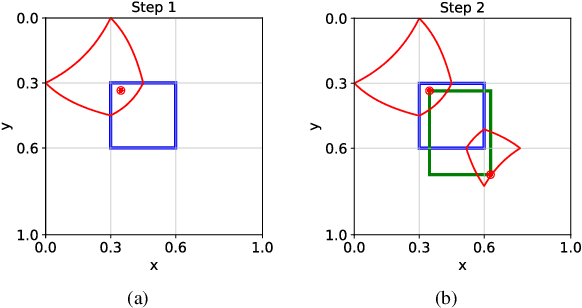
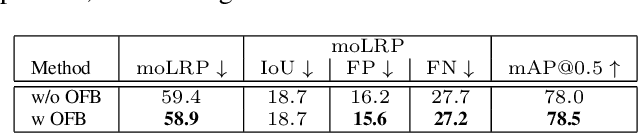
Two-stage deep object detectors generate a set of regions-of-interest (RoI) in the first stage, then, in the second stage, identify objects among the proposed RoIs that sufficiently overlap with a ground truth (GT) box. The second stage is known to suffer from a bias towards RoIs that have low intersection-over-union (IoU) with the associated GT boxes. To address this issue, we first propose a sampling method to generate bounding boxes (BB) that overlap with a given reference box more than a given IoU threshold. Then, we use this BB generation method to develop a positive RoI (pRoI) generator that produces RoIs following any desired spatial or IoU distribution, for the second-stage. We show that our pRoI generator is able to simulate other sampling methods for positive examples such as hard example mining and prime sampling. Using our generator as an analysis tool, we show that (i) IoU imbalance has an adverse effect on performance, (ii) hard positive example mining improves the performance only for certain input IoU distributions, and (iii) the imbalance among the foreground classes has an adverse effect on performance and that it can be alleviated at the batch level. Finally, we train Faster R-CNN using our pRoI generator and, compared to conventional training, obtain better or on-par performance for low IoUs and significant improvements for higher IoUs (e.g. for $IoU=0.8$, $\mathrm{mAP@0.8}$ improves by $10.9\%$). The code will be made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge