Generalising Multilingual Concept-to-Text NLG with Language Agnostic Delexicalisation
Paper and Code
May 07, 2021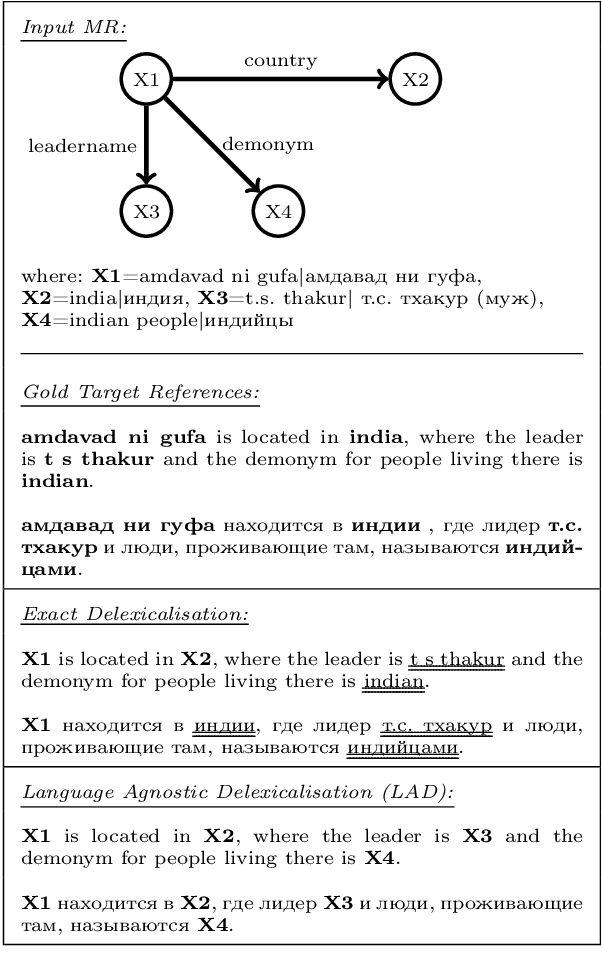
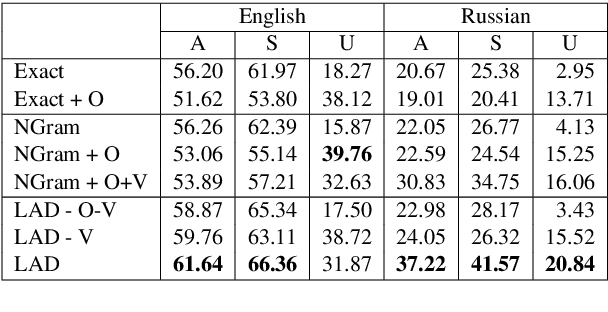
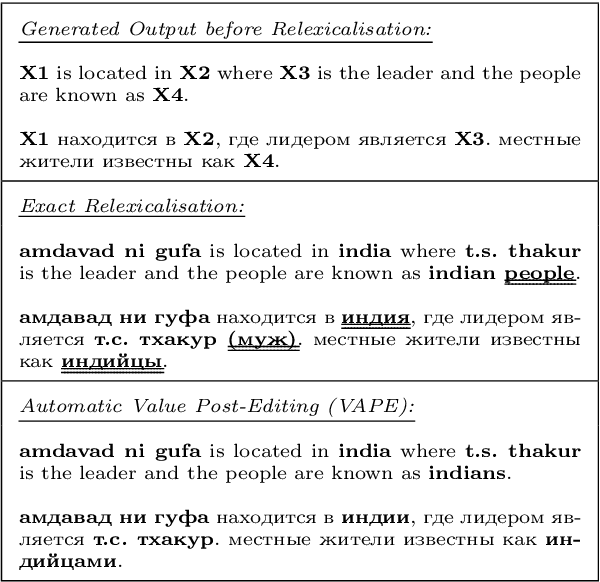
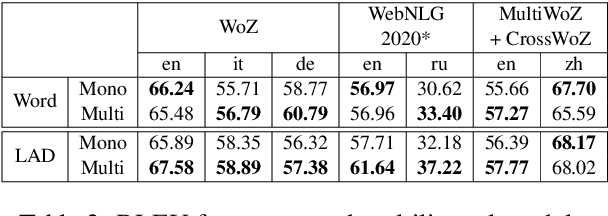
Concept-to-text Natural Language Generation is the task of expressing an input meaning representation in natural language. Previous approaches in this task have been able to generalise to rare or unseen instances by relying on a delexicalisation of the input. However, this often requires that the input appears verbatim in the output text. This poses challenges in multilingual settings, where the task expands to generate the output text in multiple languages given the same input. In this paper, we explore the application of multilingual models in concept-to-text and propose Language Agnostic Delexicalisation, a novel delexicalisation method that uses multilingual pretrained embeddings, and employs a character-level post-editing model to inflect words in their correct form during relexicalisation. Our experiments across five datasets and five languages show that multilingual models outperform monolingual models in concept-to-text and that our framework outperforms previous approaches, especially for low resource languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge