Gap Aware Mitigation of Gradient Staleness
Paper and Code
Sep 25, 2019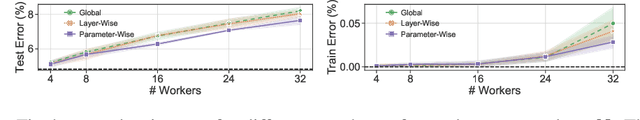
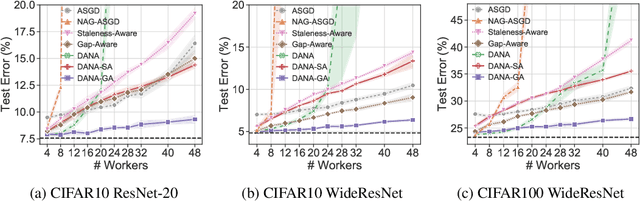
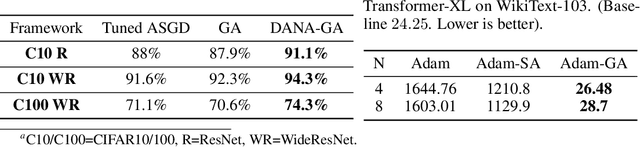
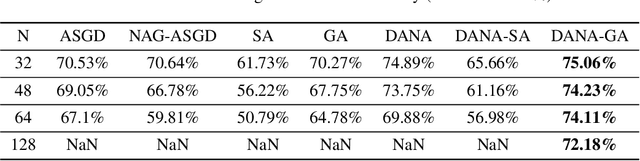
Cloud computing is becoming increasingly popular as a platform for distributed training of deep neural networks. Synchronous stochastic gradient descent (SSGD) suffers from substantial slowdowns due to stragglers if the environment is non-dedicated, as is common in cloud computing. Asynchronous SGD (ASGD) methods are immune to these slowdowns but are scarcely used due to gradient staleness, which encumbers the convergence process. Recent techniques have had limited success mitigating the gradient staleness when scaling up to many workers (computing nodes). In this paper we define the Gap as a measure of gradient staleness and propose Gap-Aware (GA), a novel asynchronous-distributed method that penalizes stale gradients linearly to the Gap and performs well even when scaling to large numbers of workers. Our evaluation on the CIFAR, ImageNet, and WikiText-103 datasets shows that GA outperforms the currently acceptable gradient penalization method, in final test accuracy. We also provide convergence rate proof for GA. Despite prior beliefs, we show that if GA is applied, momentum becomes beneficial in asynchronous environments, even when the number of workers scales up.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge