Fusing Interpretable Knowledge of Neural Network Learning Agents For Swarm-Guidance
Paper and Code
Apr 01, 2022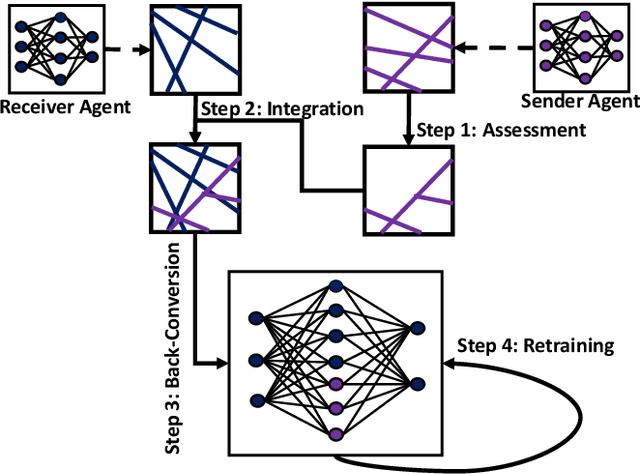
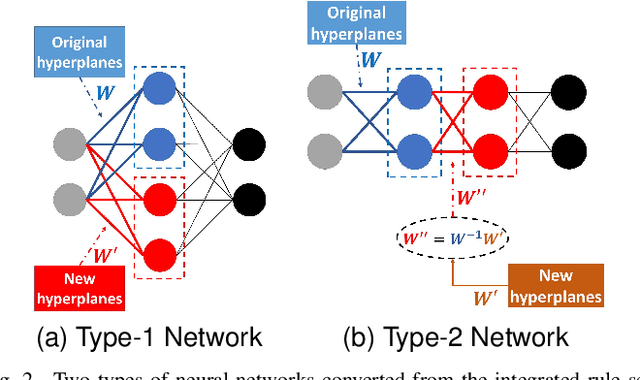
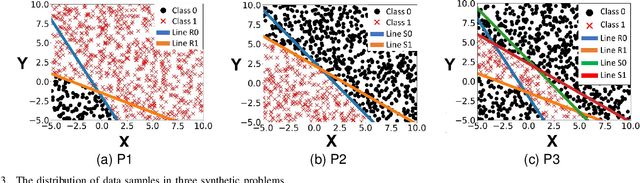
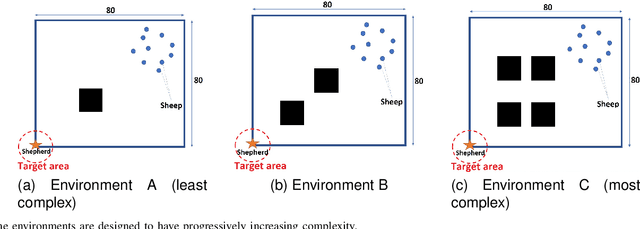
Neural-based learning agents make decisions using internal artificial neural networks. In certain situations, it becomes pertinent that this knowledge is re-interpreted in a friendly form to both the human and the machine. These situations include: when agents are required to communicate the knowledge they learn to each other in a transparent way in the presence of an external human observer, in human-machine teaming settings where humans and machines need to collaborate on a task, or where there is a requirement to verify the knowledge exchanged between the agents. We propose an interpretable knowledge fusion framework suited for neural-based learning agents, and propose a Priority on Weak State Areas (PoWSA) retraining technique. We first test the proposed framework on a synthetic binary classification task before evaluating it on a shepherding-based multi-agent swarm guidance task. Results demonstrate that the proposed framework increases the success rate on the swarm-guidance environment by 11% and better stability in return for a modest increase in computational cost of 14.5% to achieve interpretability. Moreover, the framework presents the knowledge learnt by an agent in a human-friendly representation, leading to a better descriptive visual representation of an agent's knowledge.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge