FROG: Effective Friend Recommendation in Online Games via Modality-aware User Preferences
Paper and Code
Apr 13, 2025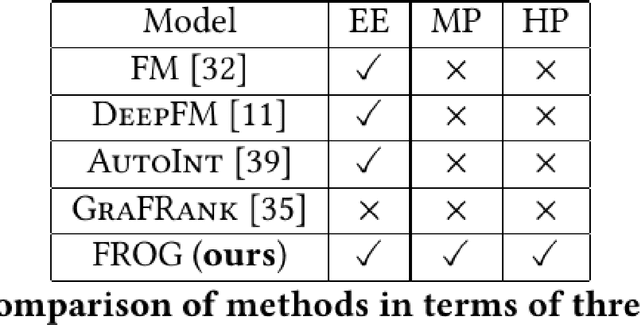
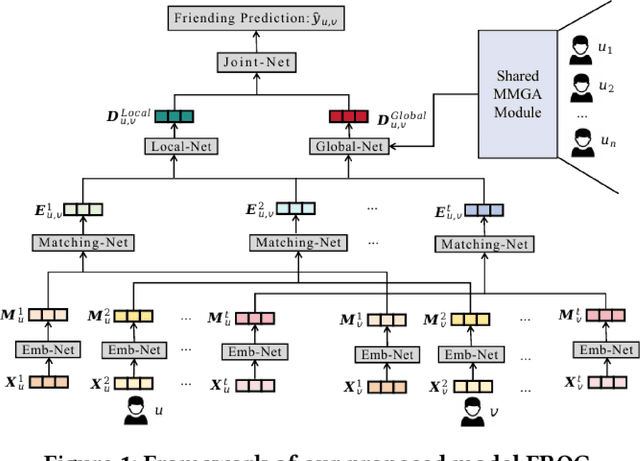
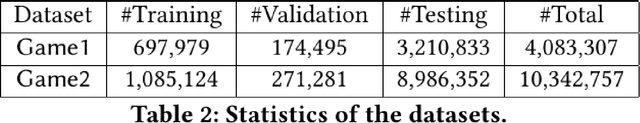
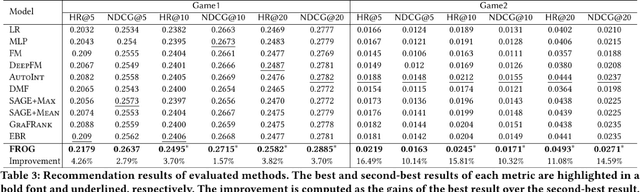
Due to the convenience of mobile devices, the online games have become an important part for user entertainments in reality, creating a demand for friend recommendation in online games. However, none of existing approaches can effectively incorporate the multi-modal user features (\emph{e.g.}, images and texts) with the structural information in the friendship graph, due to the following limitations: (1) some of them ignore the high-order structural proximity between users, (2) some fail to learn the pairwise relevance between users at modality-specific level, and (3) some cannot capture both the local and global user preferences on different modalities. By addressing these issues, in this paper, we propose an end-to-end model \textsc{FROG} that better models the user preferences on potential friends. Comprehensive experiments on both offline evaluation and online deployment at \kw{Tencent} have demonstrated the superiority of \textsc{FROG} over existing approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge