Frequency Explains the Inverse Correlation of Large Language Models' Size, Training Data Amount, and Surprisal's Fit to Reading Times
Paper and Code
Feb 03, 2024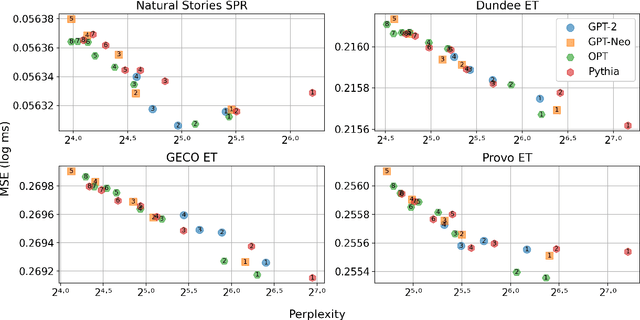

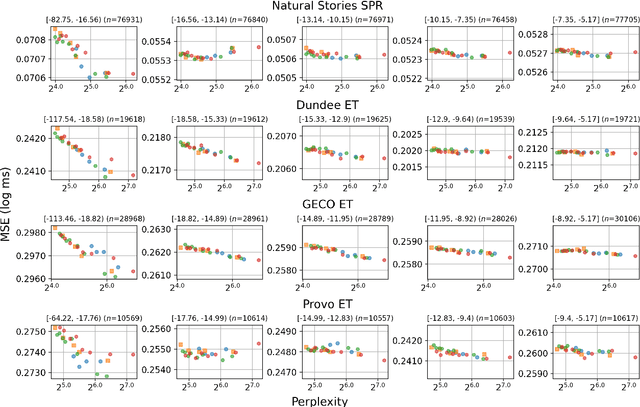
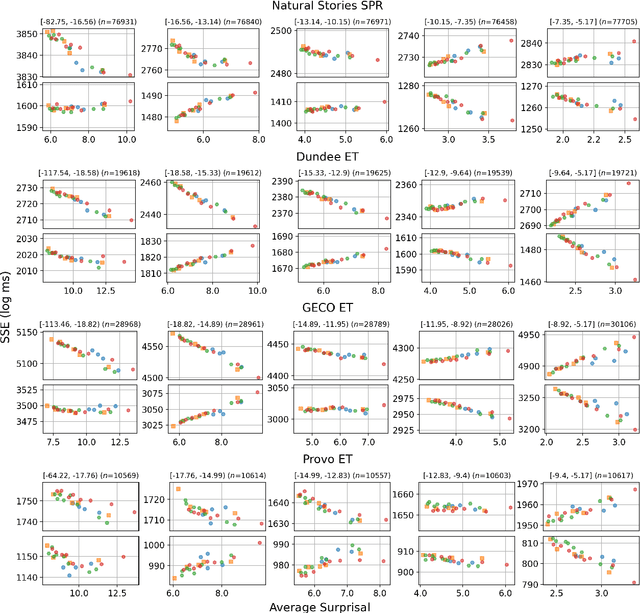
Recent studies have shown that as Transformer-based language models become larger and are trained on very large amounts of data, the fit of their surprisal estimates to naturalistic human reading times degrades. The current work presents a series of analyses showing that word frequency is a key explanatory factor underlying these two trends. First, residual errors from four language model families on four corpora show that the inverse correlation between model size and fit to reading times is the strongest on the subset of least frequent words, which is driven by excessively accurate predictions of larger model variants. Additionally, training dynamics reveal that during later training steps, all model variants learn to predict rare words and that larger model variants do so more accurately, which explains the detrimental effect of both training data amount and model size on fit to reading times. Finally, a feature attribution analysis demonstrates that larger model variants are able to accurately predict rare words based on both an effectively longer context window size as well as stronger local associations compared to smaller model variants. Taken together, these results indicate that Transformer-based language models' surprisal estimates diverge from human-like expectations due to the superhumanly complex associations they learn for predicting rare words.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge