Fraud Detection in Networks: State-of-the-art
Paper and Code
Oct 24, 2019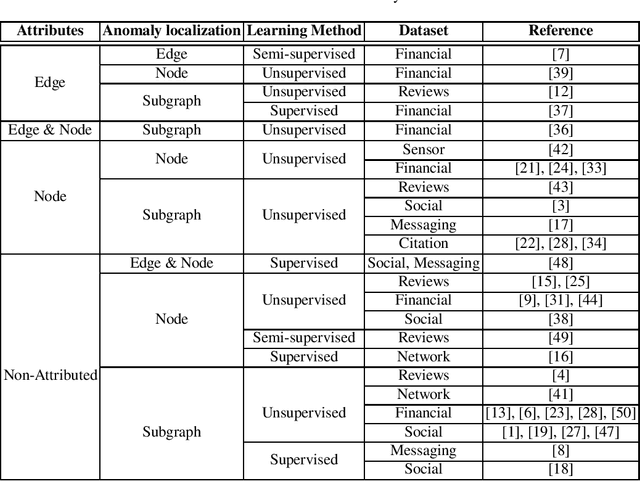
Financial fraud detection represents the challenge of finding anomalies in networks of financial transactions. In general, the anomaly detection (AD) is the problem of distinguishing between normal data samples with well defined patterns or signatures and those that do not conform to the expected profiles. The fraudulent behaviour in money laundering may manifest itself through unusual patterns in financial transaction networks. In such networks, nodes represents customers and the edges are transactions: a directed edge between two nodes illustrates that there is a money transfer in the respective direction, where the weight on the edge is the transferred amount. In this paper we present a survey on the fundamental anomaly detection techniques and then present briefly the relevant literature in connection with fraud detection context.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge