Forecasting localized weather impacts on vegetation as seen from space with meteo-guided video prediction
Paper and Code
Mar 28, 2023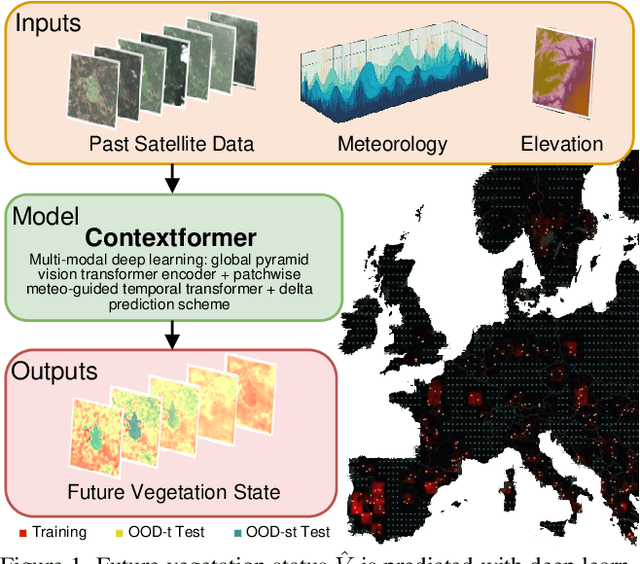
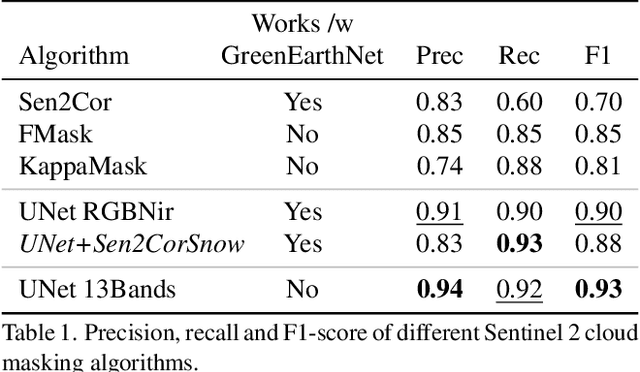

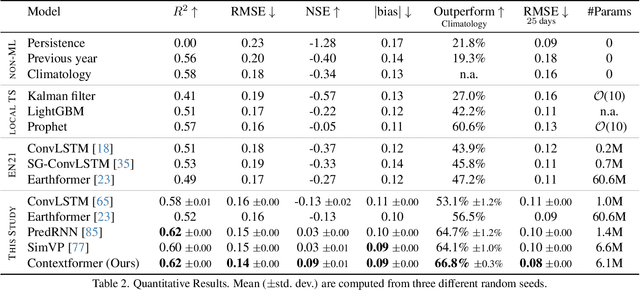
We present a novel approach for modeling vegetation response to weather in Europe as measured by the Sentinel 2 satellite. Existing satellite imagery forecasting approaches focus on photorealistic quality of the multispectral images, while derived vegetation dynamics have not yet received as much attention. We leverage both spatial and temporal context by extending state-of-the-art video prediction methods with weather guidance. We extend the EarthNet2021 dataset to be suitable for vegetation modeling by introducing a learned cloud mask and an appropriate evaluation scheme. Qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate superior performance of our approach over a wide variety of baseline methods, including leading approaches to satellite imagery forecasting. Additionally, we show how our modeled vegetation dynamics can be leveraged in a downstream task: inferring gross primary productivity for carbon monitoring. To the best of our knowledge, this work presents the first models for continental-scale vegetation modeling at fine resolution able to capture anomalies beyond the seasonal cycle, thereby paving the way for predictive assessments of vegetation status.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge