ForcePose: A Deep Learning Approach for Force Calculation Based on Action Recognition Using MediaPipe Pose Estimation Combined with Object Detection
Paper and Code
Mar 28, 2025

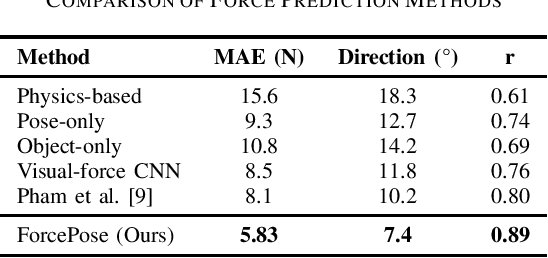

Force estimation in human-object interactions is crucial for various fields like ergonomics, physical therapy, and sports science. Traditional methods depend on specialized equipment such as force plates and sensors, which makes accurate assessments both expensive and restricted to laboratory settings. In this paper, we introduce ForcePose, a novel deep learning framework that estimates applied forces by combining human pose estimation with object detection. Our approach leverages MediaPipe for skeletal tracking and SSD MobileNet for object recognition to create a unified representation of human-object interaction. We've developed a specialized neural network that processes both spatial and temporal features to predict force magnitude and direction without needing any physical sensors. After training on our dataset of 850 annotated videos with corresponding force measurements, our model achieves a mean absolute error of 5.83 N in force magnitude and 7.4 degrees in force direction. When compared to existing computer vision approaches, our method performs 27.5% better while still offering real-time performance on standard computing hardware. ForcePose opens up new possibilities for force analysis in diverse real-world scenarios where traditional measurement tools are impractical or intrusive. This paper discusses our methodology, the dataset creation process, evaluation metrics, and potential applications across rehabilitation, ergonomics assessment, and athletic performance analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge