Fooling SHAP with Stealthily Biased Sampling
Paper and Code
May 30, 2022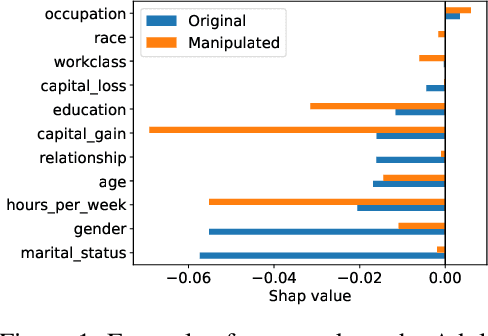
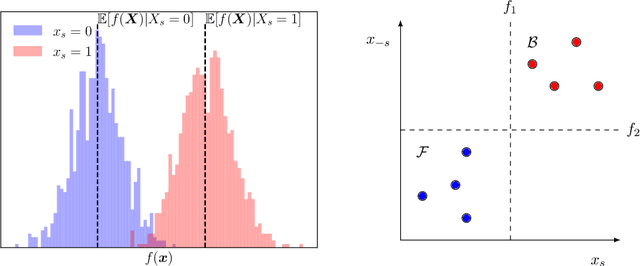

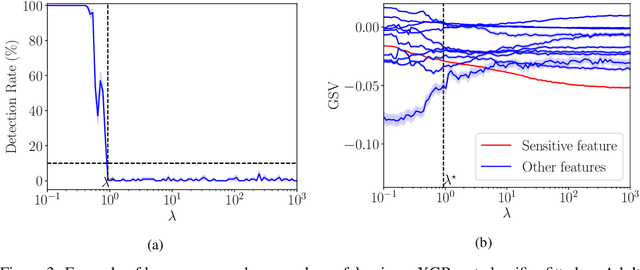
SHAP explanations aim at identifying which features contribute the most to the difference in model prediction at a specific input versus a background distribution. Recent studies have shown that they can be manipulated by malicious adversaries to produce arbitrary desired explanations. However, existing attacks focus solely on altering the black-box model itself. In this paper, we propose a complementary family of attacks that leave the model intact and manipulate SHAP explanations using stealthily biased sampling of the data points used to approximate expectations w.r.t the background distribution. In the context of fairness audit, we show that our attack can reduce the importance of a sensitive feature when explaining the difference in outcomes between groups, while remaining undetected. These results highlight the manipulability of SHAP explanations and encourage auditors to treat post-hoc explanations with skepticism.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge