Fooling Computer Vision into Inferring the Wrong Body Mass Index
Paper and Code
May 16, 2019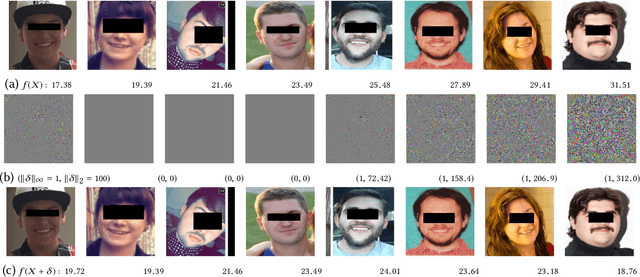
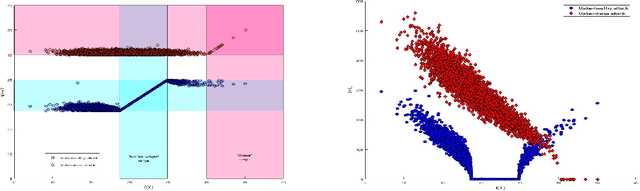
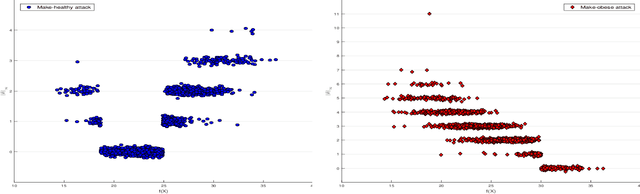
Recently it's been shown that neural networks can use images of human faces to accurately predict Body Mass Index (BMI), a widely used health indicator. In this paper we demonstrate that a neural network performing BMI inference is indeed vulnerable to test-time adversarial attacks. This extends test-time adversarial attacks from classification tasks to regression. The application we highlight is BMI inference in the insurance industry, where such adversarial attacks imply a danger of insurance fraud.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge