FocalGatedNet: A Novel Deep Learning Model for Accurate Knee Joint Angle Prediction
Paper and Code
Jun 12, 2023


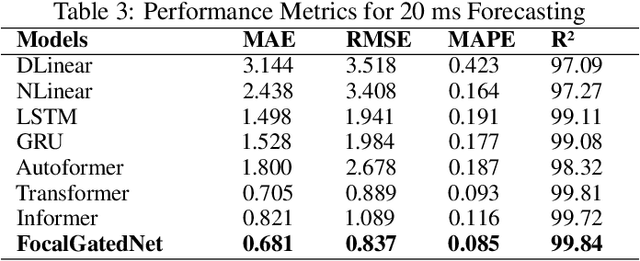
Predicting knee joint angles accurately is critical for biomechanical analysis and rehabilitation. This paper introduces a new deep learning model called FocalGatedNet that incorporates Dynamic Contextual Focus (DCF) Attention and Gated Linear Units (GLU) to enhance feature dependencies and interactions. Our proposed model is evaluated on a large-scale dataset and compared to existing models such as Transformer, Autoformer, Informer, NLinear, DLinear, and LSTM in multi-step gait trajectory prediction. Our results demonstrate that FocalGatedNet outperforms other state-of-the-art models for long-term prediction lengths (60 ms, 80 ms, and 100 ms), achieving an average improvement of 13.66% in MAE and 8.13% in RMSE compared to the second-best performing model (Transformer). Furthermore, our model has a lower computational load than most equivalent deep learning models. These results highlight the effectiveness of our proposed model for knee joint angle prediction and the importance of our modifications for this specific application.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge