Flexible Transmitter Network
Paper and Code
Apr 10, 2020


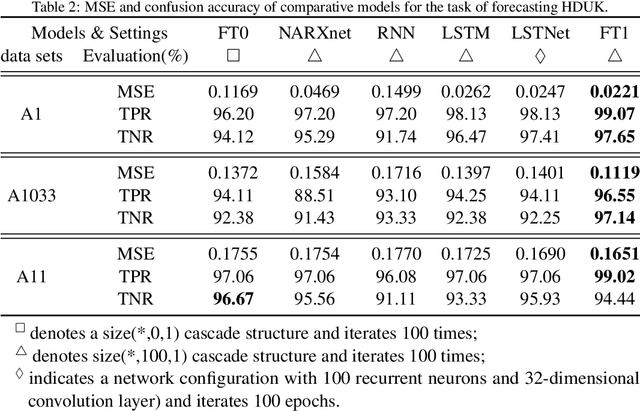
Current neural networks are mostly built upon the MP model, which usually formulates the neuron as executing an activation function on the real-valued weighted aggregation of signals received from other neurons. In this paper, we propose the Flexible Transmitter (FT) model, a novel bio-plausible neuron with flexible plasticity. The FT model employs a pair of parameters to model the transmitter between neurons and sets up a neurotransmitter regulated memory unit to record the long-term learning information of the concerned neuron, thus leading to the formulation of the FT model as a two-variable two-valued function, which takes the commonly-used MP neuron model as its special case. The FT model can handle more complicated data, even time series signals. To exhibit the power and potential of our FT model, we present the Flexible Transmitter Network (FTNet), which is built in the most common fully-connected feed-forward architecture by incorporating the FT neuron as the basic building block. FTNet allows gradient calculation and can be implemented by an extension of the backpropagation algorithm in the complex domain. Experiments on a board range of tasks show the superiority of the proposed FTNet. This study provides an alternative basic building block in neural networks and exhibits the feasibility of developing artificial neural networks with neuronal plasticity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge