Flashlight Search Medial Axis: A Pixel-Free Pore-Network Extraction Algorithm
Paper and Code
Aug 05, 2023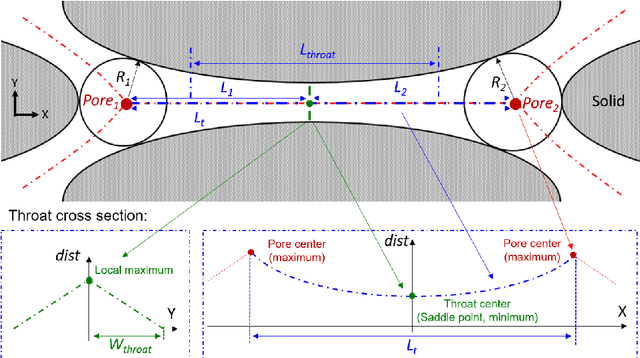
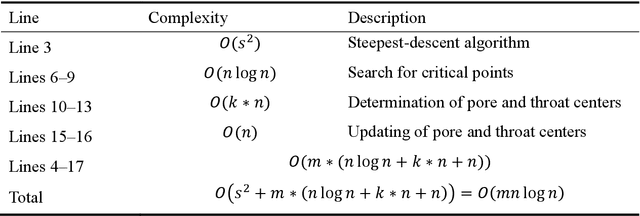
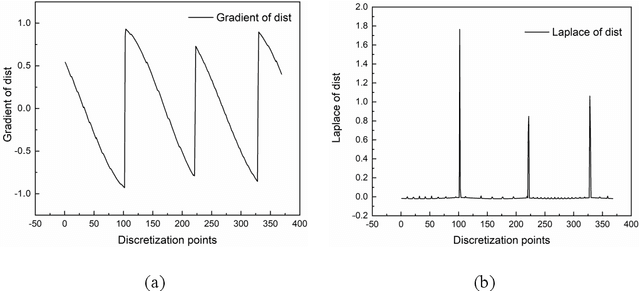
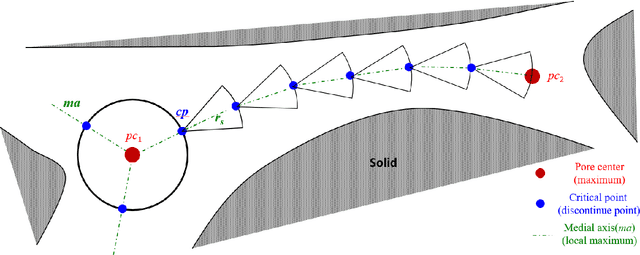
Pore-network models (PNMs) have become an important tool in the study of fluid flow in porous media over the last few decades, and the accuracy of their results highly depends on the extraction of pore networks. Traditional methods of pore-network extraction are based on pixels and require images with high quality. Here, a pixel-free method called the flashlight search medial axis (FSMA) algorithm is proposed for pore-network extraction in a continuous space. The search domain in a two-dimensional space is a line, whereas a surface domain is searched in a three-dimensional scenario. Thus, the FSMA algorithm follows the dimensionality reduction idea; the medial axis can be identified using only a few points instead of calculating every point in the void space. In this way, computational complexity of this method is greatly reduced compared to that of traditional pixel-based extraction methods, thus enabling large-scale pore-network extraction. Based on cases featuring two- and three-dimensional porous media, the FSMA algorithm performs well regardless of the topological structure of the pore network or the positions of the pore and throat centers. This algorithm can also be used to examine both closed- and open-boundary cases. Finally, the FSMA algorithm can search dead-end pores, which is of great significance in the study of multiphase flow in porous media.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge