First-Order Statistical Framework for Multi-Channel Passive Detection
Paper and Code
Feb 14, 2023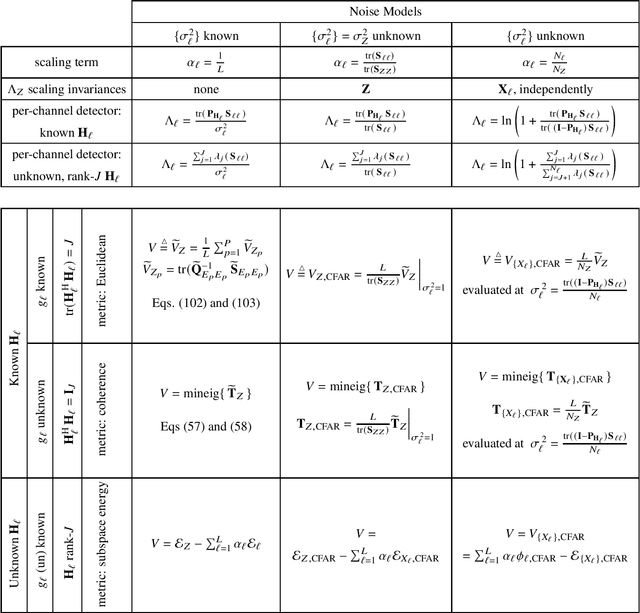
In this paper we establish a general first-order statistical framework for the detection of a common signal impinging on spatially distributed receivers. We consider three types of channel models: 1) the propagation channel is completely known, 2) the propagation is known but channel gains are unknown, and 3) the propagation channel is unknown. For each problem, we address the cases of a) known noise variances, b) common but unknown noise variances, and c) different and unknown noise variances. For all 9 cases, we establish generalized-likelihood-ratio (GLR) detectors, and show that each one can be decomposed into two terms. The first term is a weighted combination of the GLR detectors that arise from considering each channel separately. This result is then modified by a fusion or cross-validation term, which expresses the level of confidence that the single-channel detectors have detected a common source. Of particular note are the constant false-alarm rate (CFAR) detectors that allow for scale-invariant detection in multiple channels with different noise powers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge