First Arrival Position in Molecular Communication Via Generator of Diffusion Semigroup
Paper and Code
Jan 14, 2022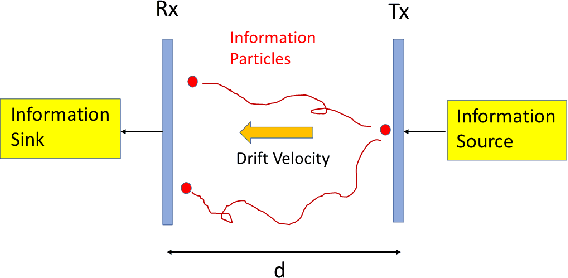
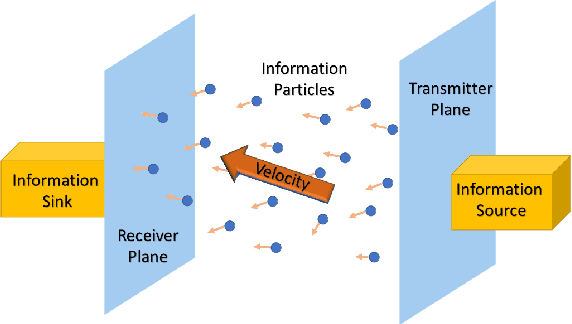
We consider the problem of characterizing the first arrival position (FAP) density in molecular communication (MC) with a diffusion-advection channel that permits a constant drift velocity pointed to arbitrary direction. The advantage of FAP modulation lies in the fact that it could encode more information into higher dimensional spatial variables, compared to other modulation techniques using time or molecule numbers. However, effective methods to characterize the FAP density in a general framework do not exist. In this paper, we devise a methodology that fully resolves the FAP density with planar absorbing receivers in arbitrary dimensions. Our work recovers existing results of FAP in 2D and 3D as special cases. The key insight of our approach is to remove the time dependence of the MC system evolution based on the generator of diffusion semigroups.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge