Finding Inverse Document Frequency Information in BERT
Paper and Code
Feb 24, 2022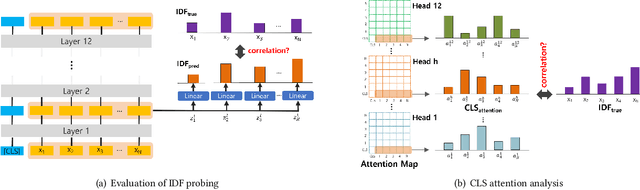
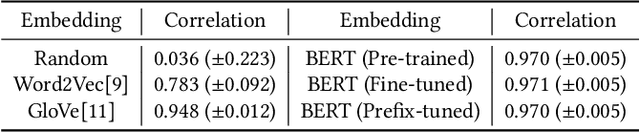
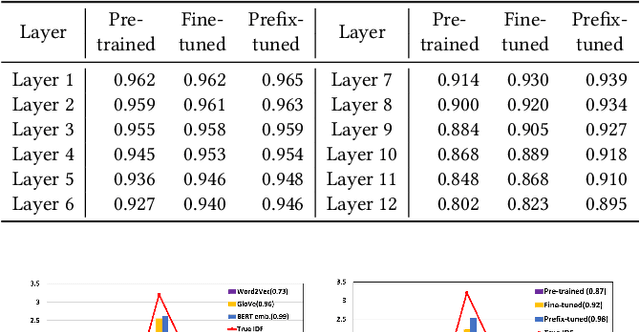

For many decades, BM25 and its variants have been the dominant document retrieval approach, where their two underlying features are Term Frequency (TF) and Inverse Document Frequency (IDF). The traditional approach, however, is being rapidly replaced by Neural Ranking Models (NRMs) that can exploit semantic features. In this work, we consider BERT-based NRMs and study if IDF information is present in the NRMs. This simple question is interesting because IDF has been indispensable for the traditional lexical matching, but global features like IDF are not explicitly learned by neural language models including BERT. We adopt linear probing as the main analysis tool because typical BERT based NRMs utilize linear or inner-product based score aggregators. We analyze input embeddings, representations of all BERT layers, and the self-attention weights of CLS. By studying MS-MARCO dataset with three BERT-based models, we show that all of them contain information that is strongly dependent on IDF.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge