Feedbackward Decoding for Semantic Segmentation
Paper and Code
Aug 22, 2019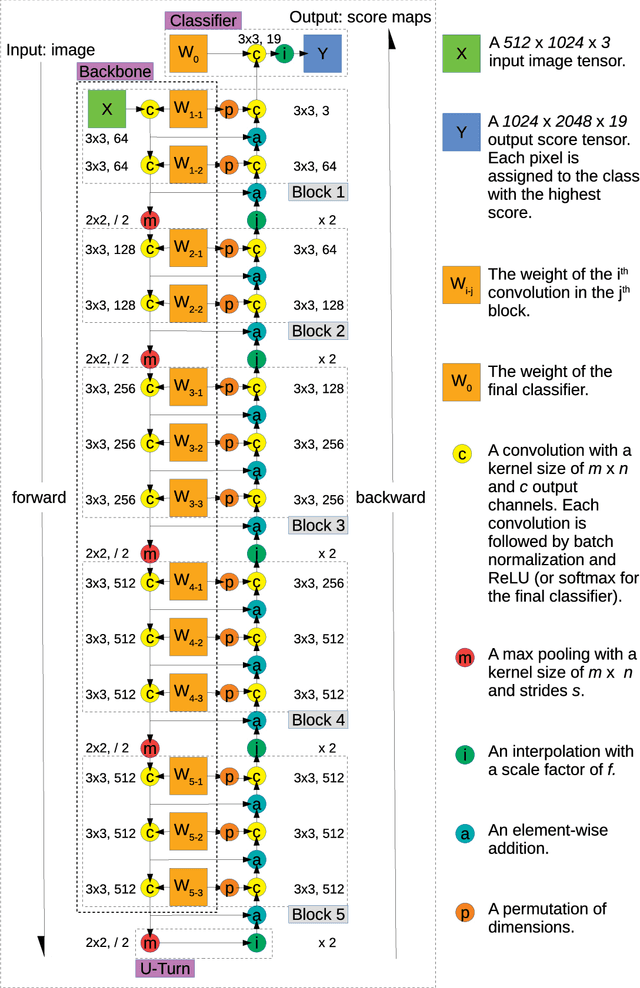
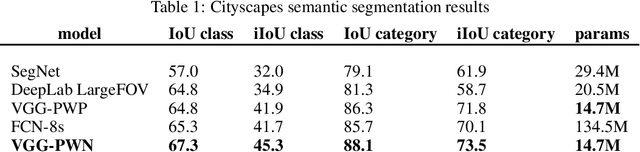
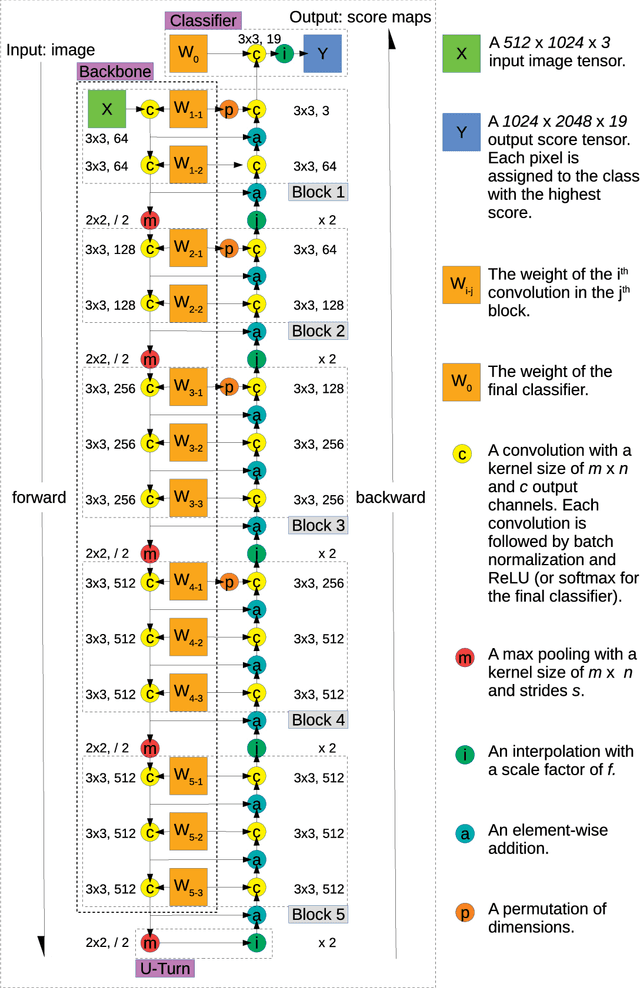
We propose a novel approach for semantic segmentation that uses an encoder in the reverse direction to decode. Many semantic segmentation networks adopt a feedforward encoder-decoder architecture. Typically, an input is first downsampled by the encoder to extract high-level semantic features and continues to be fed forward through the decoder module to recover low-level spatial clues. Our method works in an alternative direction that lets information flow backward from the last layer of the encoder towards the first. The encoder performs encoding in the forward pass and the same network performs decoding in the backward pass. Therefore, the encoder itself is also the decoder. Compared to conventional encoder-decoder architectures, ours doesn't require additional layers for decoding and further reuses the encoder weights thereby reducing the total number of parameters required for processing. We show by using only the 13 convolutional layers from VGG-16 plus one tiny classification layer, our model significantly outperforms other frequently cited models that are also adapted from VGG-16. On the Cityscapes semantic segmentation benchmark, our model uses 50.0% less parameters than SegNet and achieves an 18.1% higher "IoU class" score; it uses 28.3% less parameters than DeepLab LargeFOV and the achieved "IoU class" score is 3.9% higher; it uses 89.1% fewer parameters than FCN-8s and the achieved "IoU class" score is 3.1% higher. Our code will be publicly available on Github later.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge