FedFMC: Sequential Efficient Federated Learning on Non-iid Data
Paper and Code
Jun 19, 2020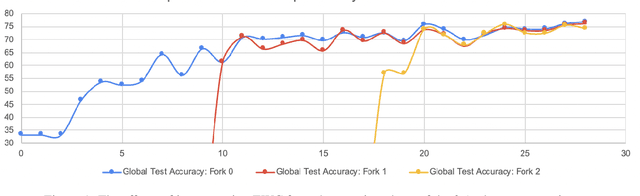
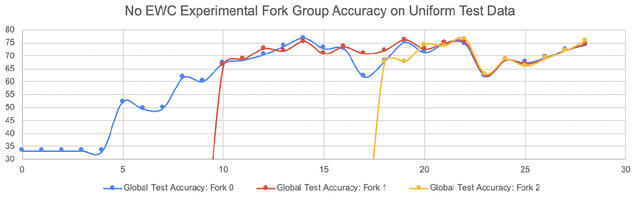
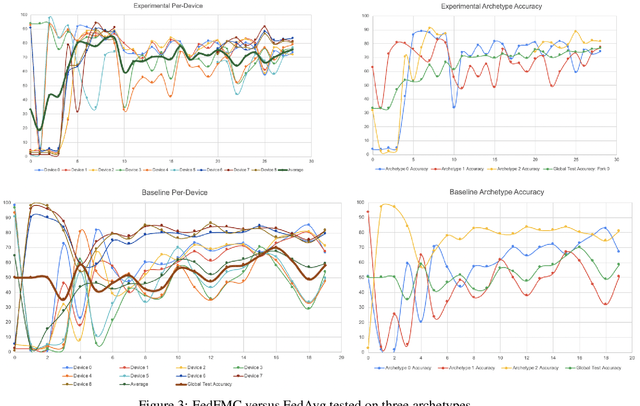
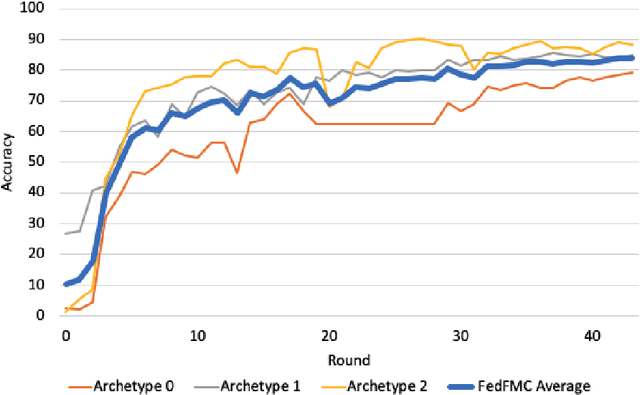
As a mechanism for devices to update a global model without sharing data, federated learning bridges the tension between the need for data and respect for privacy. However, classic FL methods like Federated Averaging struggle with non-iid data, a prevalent situation in the real world. Previous solutions are sub-optimal as they either employ a small shared global subset of data or greater number of models with increased communication costs. We propose FedFMC (Fork-Merge-Consolidate), a method that dynamically forks devices into updating different global models then merges and consolidates separate models into one. We first show the soundness of FedFMC on simple datasets, then run several experiments comparing against baseline approaches. These experiments show that FedFMC substantially improves upon earlier approaches to non-iid data in the federated learning context without using a globally shared subset of data nor increase communication costs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge