Federated Learning over a Wireless Network: Distributed User Selection through Random Access
Paper and Code
Jul 07, 2023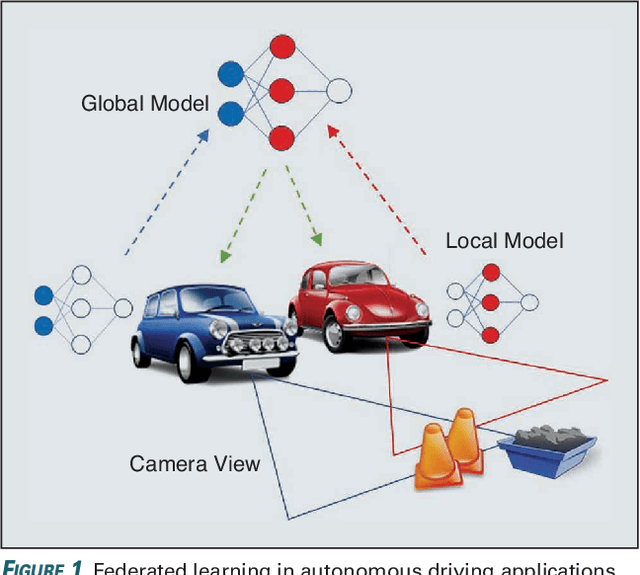
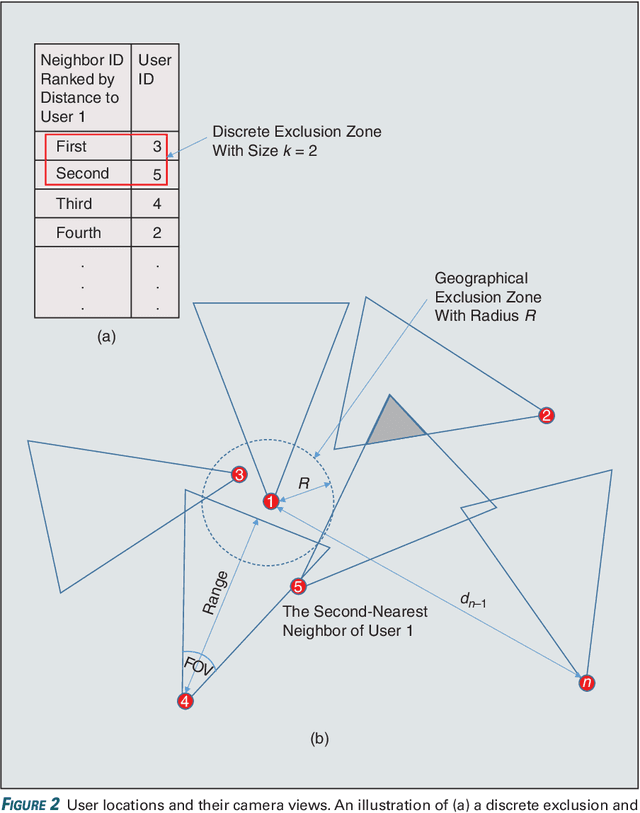
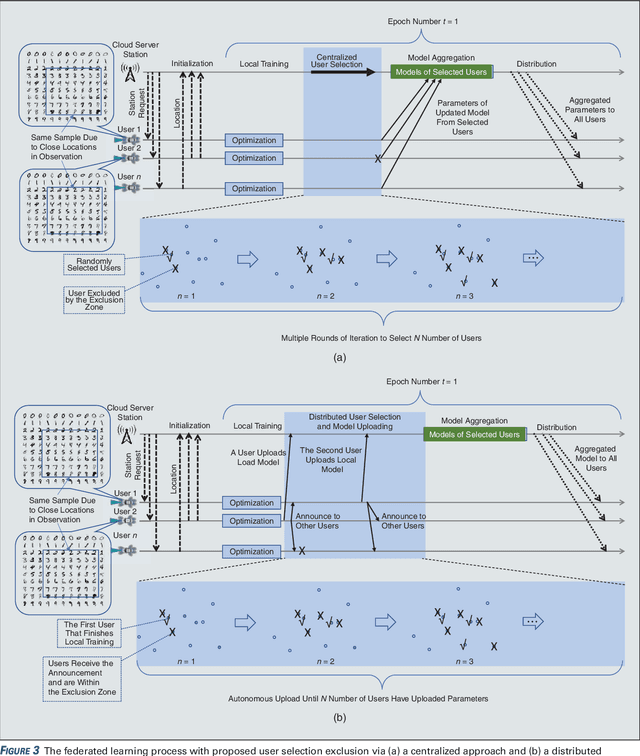
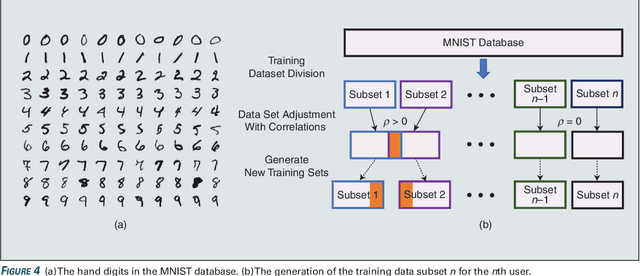
User selection has become crucial for decreasing the communication costs of federated learning (FL) over wireless networks. However, centralized user selection causes additional system complexity. This study proposes a network intrinsic approach of distributed user selection that leverages the radio resource competition mechanism in random access. Taking the carrier sensing multiple access (CSMA) mechanism as an example of random access, we manipulate the contention window (CW) size to prioritize certain users for obtaining radio resources in each round of training. Training data bias is used as a target scenario for FL with user selection. Prioritization is based on the distance between the newly trained local model and the global model of the previous round. To avoid excessive contribution by certain users, a counting mechanism is used to ensure fairness. Simulations with various datasets demonstrate that this method can rapidly achieve convergence similar to that of the centralized user selection approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge