Feature-Aligned Video Raindrop Removal with Temporal Constraints
Paper and Code
May 29, 2022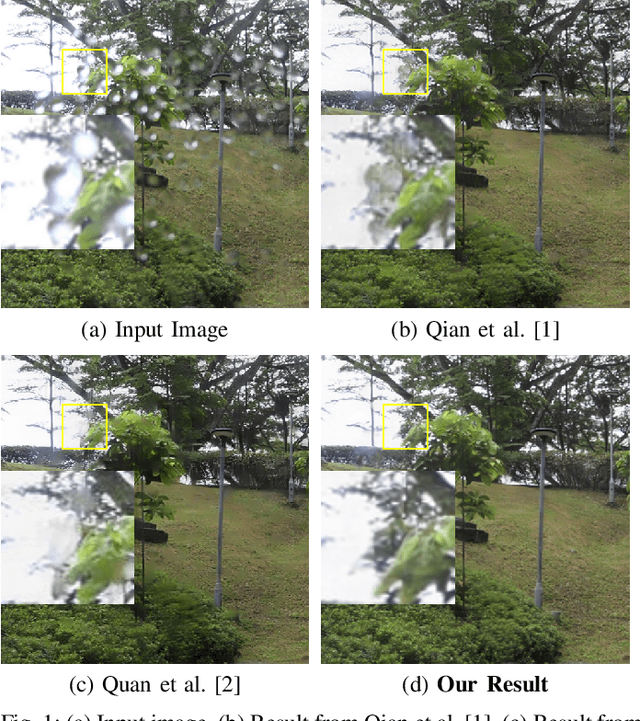
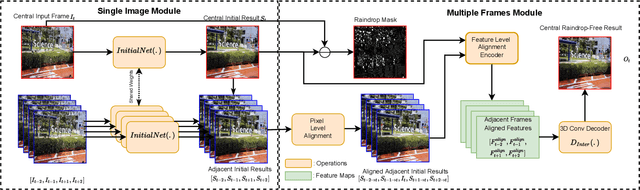
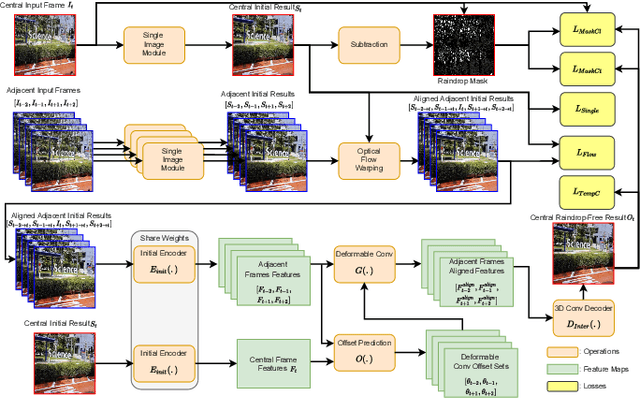
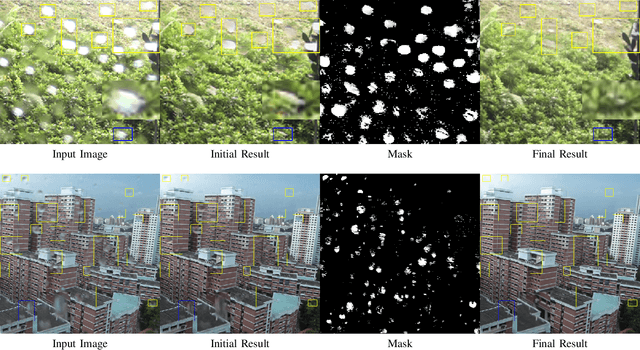
Existing adherent raindrop removal methods focus on the detection of the raindrop locations, and then use inpainting techniques or generative networks to recover the background behind raindrops. Yet, as adherent raindrops are diverse in sizes and appearances, the detection is challenging for both single image and video. Moreover, unlike rain streaks, adherent raindrops tend to cover the same area in several frames. Addressing these problems, our method employs a two-stage video-based raindrop removal method. The first stage is the single image module, which generates initial clean results. The second stage is the multiple frame module, which further refines the initial results using temporal constraints, namely, by utilizing multiple input frames in our process and applying temporal consistency between adjacent output frames. Our single image module employs a raindrop removal network to generate initial raindrop removal results, and create a mask representing the differences between the input and initial output. Once the masks and initial results for consecutive frames are obtained, our multiple-frame module aligns the frames in both the image and feature levels and then obtains the clean background. Our method initially employs optical flow to align the frames, and then utilizes deformable convolution layers further to achieve feature-level frame alignment. To remove small raindrops and recover correct backgrounds, a target frame is predicted from adjacent frames. A series of unsupervised losses are proposed so that our second stage, which is the video raindrop removal module, can self-learn from video data without ground truths. Experimental results on real videos demonstrate the state-of-art performance of our method both quantitatively and qualitatively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge