FastVC: Fast Voice Conversion with non-parallel data
Paper and Code
Oct 08, 2020

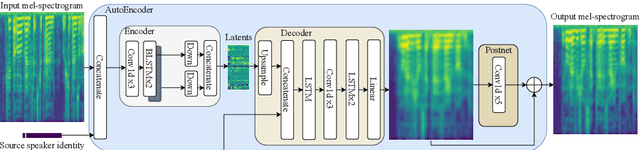
This paper introduces FastVC, an end-to-end model for fast Voice Conversion (VC). The proposed model can convert speech of arbitrary length from multiple source speakers to multiple target speakers. FastVC is based on a conditional AutoEncoder (AE) trained on non-parallel data and requires no annotations at all. This model's latent representation is shown to be speaker-independent and similar to phonemes, which is a desirable feature for VC systems. While the current VC systems primarily focus on achieving the highest overall speech quality, this paper tries to balance the development concerning resources needed to run the systems. Despite the simple structure of the proposed model, it outperforms the VC Challenge 2020 baselines on the cross-lingual task in terms of naturalness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge