Fast Simultaneous Gravitational Alignment of Multiple Point Sets
Paper and Code
Jun 21, 2021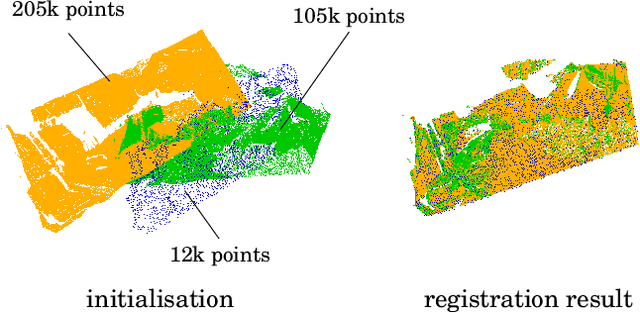
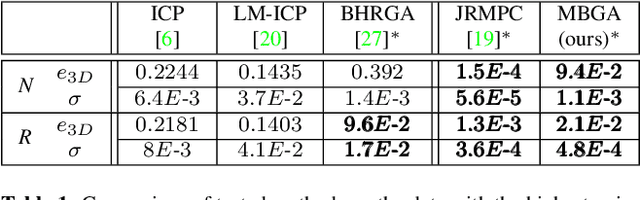
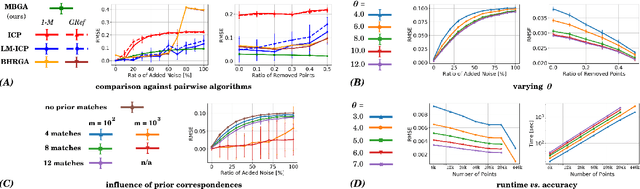
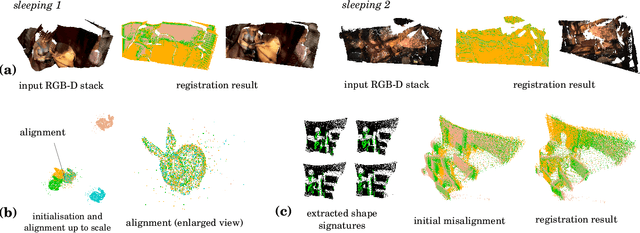
The problem of simultaneous rigid alignment of multiple unordered point sets which is unbiased towards any of the inputs has recently attracted increasing interest, and several reliable methods have been newly proposed. While being remarkably robust towards noise and clustered outliers, current approaches require sophisticated initialisation schemes and do not scale well to large point sets. This paper proposes a new resilient technique for simultaneous registration of multiple point sets by interpreting the latter as particle swarms rigidly moving in the mutually induced force fields. Thanks to the improved simulation with altered physical laws and acceleration of globally multiply-linked point interactions with a 2^D-tree (D is the space dimensionality), our Multi-Body Gravitational Approach (MBGA) is robust to noise and missing data while supporting more massive point sets than previous methods (with 10^5 points and more). In various experimental settings, MBGA is shown to outperform several baseline point set alignment approaches in terms of accuracy and runtime. We make our source code available for the community to facilitate the reproducibility of the results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge