Fast Cross-Validation via Sequential Testing
Paper and Code
Feb 03, 2016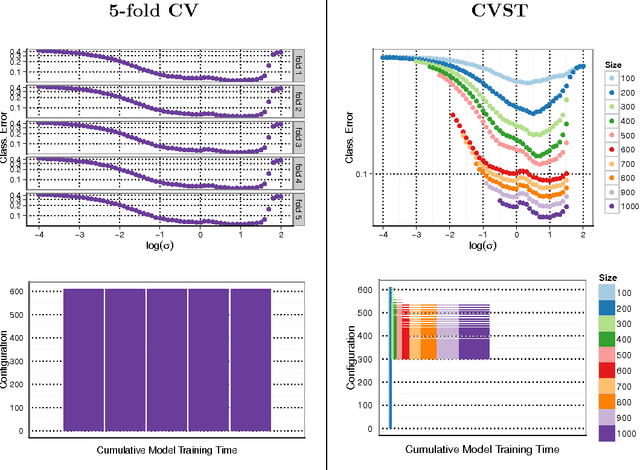



With the increasing size of today's data sets, finding the right parameter configuration in model selection via cross-validation can be an extremely time-consuming task. In this paper we propose an improved cross-validation procedure which uses nonparametric testing coupled with sequential analysis to determine the best parameter set on linearly increasing subsets of the data. By eliminating underperforming candidates quickly and keeping promising candidates as long as possible, the method speeds up the computation while preserving the capability of the full cross-validation. Theoretical considerations underline the statistical power of our procedure. The experimental evaluation shows that our method reduces the computation time by a factor of up to 120 compared to a full cross-validation with a negligible impact on the accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge