Fast algorithm for Multiple-Circle detection on images using Learning Automata
Paper and Code
May 21, 2014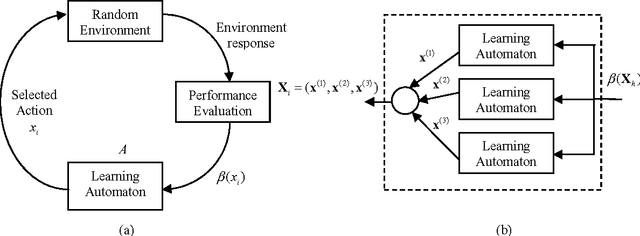
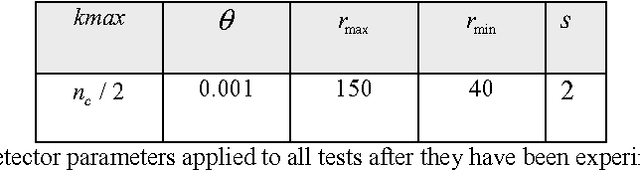
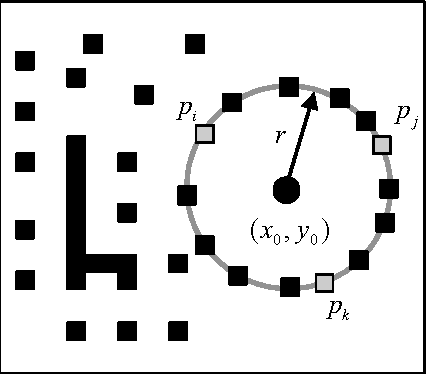
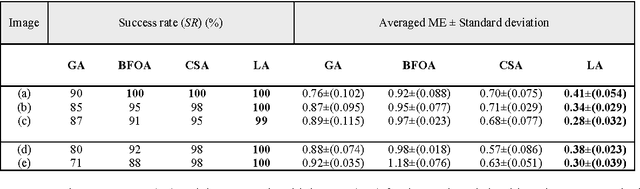
Hough transform (HT) has been the most common method for circle detection exhibiting robustness but adversely demanding a considerable computational load and large storage. Alternative approaches include heuristic methods that employ iterative optimization procedures for detecting multiple circles under the inconvenience that only one circle can be marked at each optimization cycle demanding a longer execution time. On the other hand, Learning Automata (LA) is a heuristic method to solve complex multi-modal optimization problems. Although LA converges to just one global minimum, the final probability distribution holds valuable information regarding other local minima which have emerged during the optimization process. The detection process is considered as a multi-modal optimization problem, allowing the detection of multiple circular shapes through only one optimization procedure. The algorithm uses a combination of three edge points as parameters to determine circles candidates. A reinforcement signal determines if such circle candidates are actually present at the image. Guided by the values of such reinforcement signal, the set of encoded candidate circles are evolved using the LA so that they can fit into actual circular shapes over the edge-only map of the image. The overall approach is a fast multiple-circle detector despite facing complicated conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge