FaceSaliencyAug: Mitigating Geographic, Gender and Stereotypical Biases via Saliency-Based Data Augmentation
Paper and Code
Oct 17, 2024
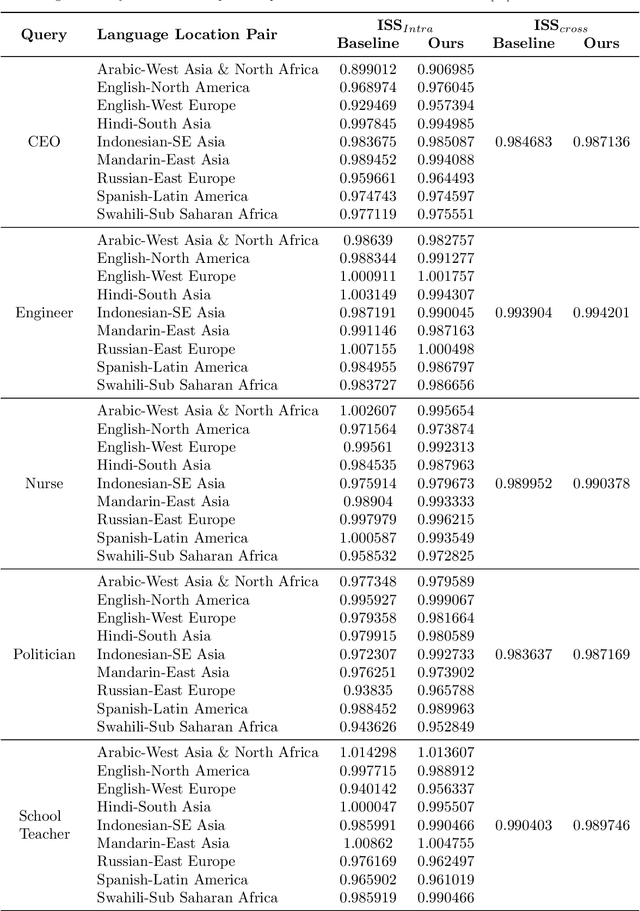
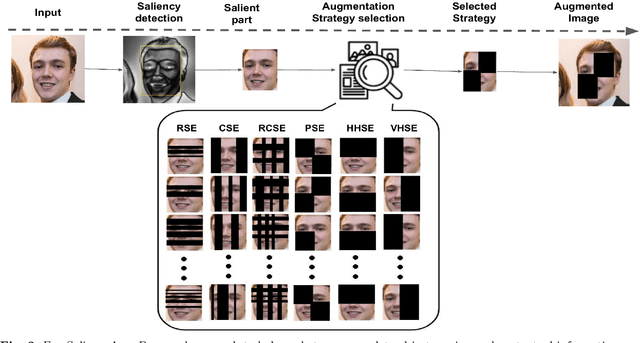
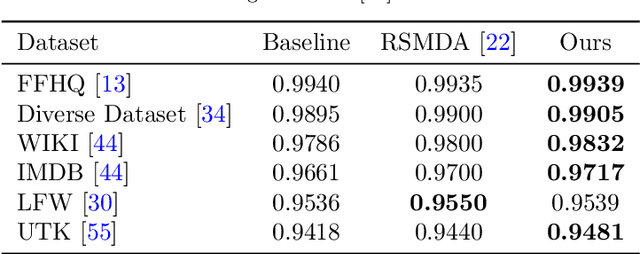
Geographical, gender and stereotypical biases in computer vision models pose significant challenges to their performance and fairness. {In this study, we present an approach named FaceSaliencyAug aimed at addressing the gender bias in} {Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Vision Transformers (ViTs). Leveraging the salient regions} { of faces detected by saliency, the propose approach mitigates geographical and stereotypical biases } {in the datasets. FaceSaliencyAug} randomly selects masks from a predefined search space and applies them to the salient region of face images, subsequently restoring the original image with masked salient region. {The proposed} augmentation strategy enhances data diversity, thereby improving model performance and debiasing effects. We quantify dataset diversity using Image Similarity Score (ISS) across five datasets, including Flickr Faces HQ (FFHQ), WIKI, IMDB, Labelled Faces in the Wild (LFW), UTK Faces, and Diverse Dataset. The proposed approach demonstrates superior diversity metrics, as evaluated by ISS-intra and ISS-inter algorithms. Furthermore, we evaluate the effectiveness of our approach in mitigating gender bias on CEO, Engineer, Nurse, and School Teacher datasets. We use the Image-Image Association Score (IIAS) to measure gender bias in these occupations. Our experiments reveal a reduction in gender bias for both CNNs and ViTs, indicating the efficacy of our method in promoting fairness and inclusivity in computer vision models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge