Exploring Uncertainty Measures for Image-Caption Embedding-and-Retrieval Task
Paper and Code
Apr 09, 2019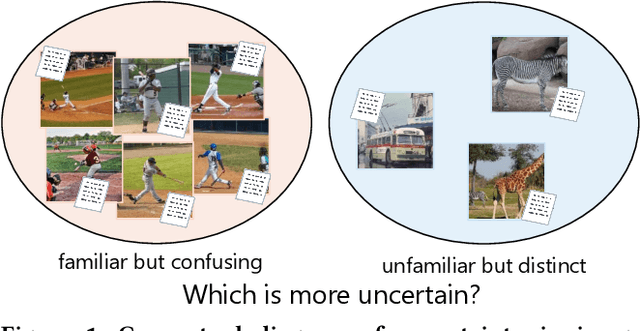
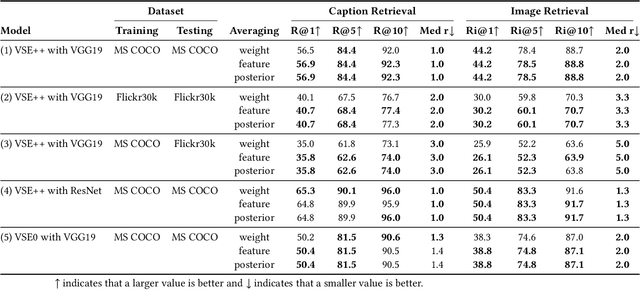
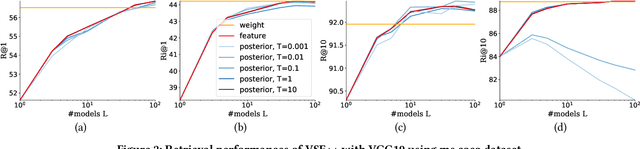
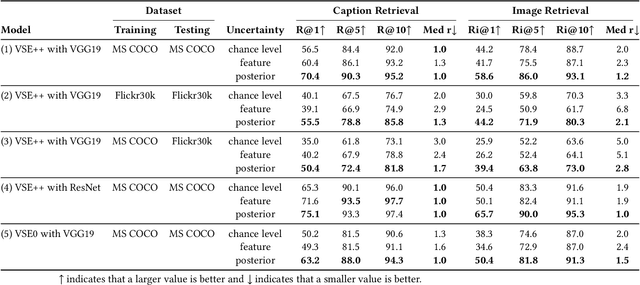
With the wide development of black-box machine learning algorithms, particularly deep neural network (DNN), the practical demand for the reliability assessment is rapidly rising. On the basis of the concept that `Bayesian deep learning knows what it does not know,' the uncertainty of DNN outputs has been investigated as a reliability measure for the classification and regression tasks. However, in the image-caption retrieval task, well-known samples are not always easy-to-retrieve samples. This study investigates two aspects of image-caption embedding-and-retrieval systems. On one hand, we quantify feature uncertainty by considering image-caption embedding as a regression task, and use it for model averaging, which can improve the retrieval performance. On the other hand, we further quantify posterior uncertainty by considering the retrieval as a classification task, and use it as a reliability measure, which can greatly improve the retrieval performance by rejecting uncertain queries. The consistent performance of two uncertainty measures is observed with different datasets (MS COCO and Flickr30k), different deep learning architectures (dropout and batch normalization), and different similarity functions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge