Exploring the impact of low-rank adaptation on the performance, efficiency, and regularization of RLHF
Paper and Code
Sep 16, 2023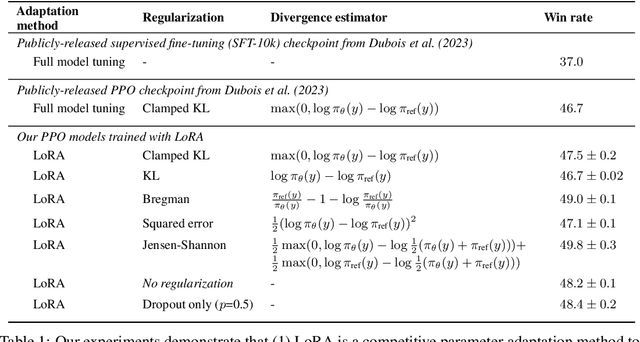
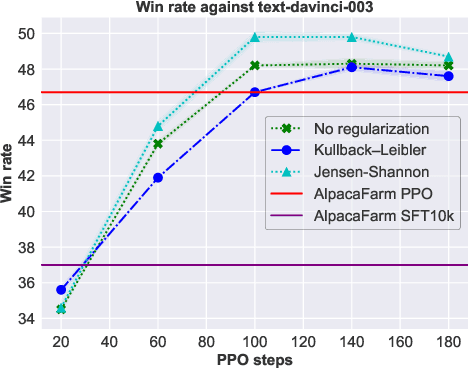
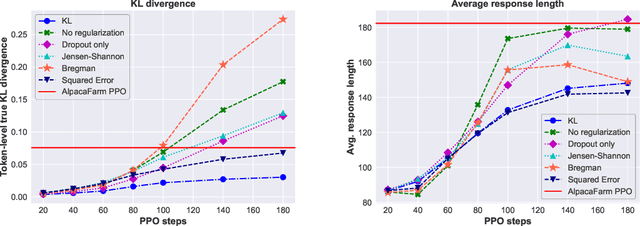
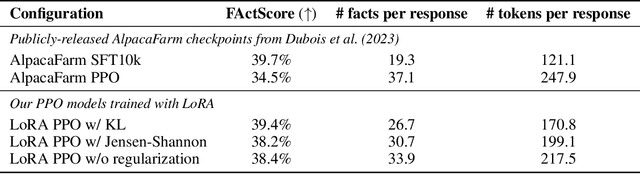
During the last stage of RLHF, a large language model is aligned to human intents via PPO training, a process that generally requires large-scale computational resources. In this technical report, we empirically investigate an efficient implementation of RLHF using low-rank adaptation (LoRA), which allows us to align the LLaMA 7B checkpoint on the Alpaca dataset using only two A100 GPUs instead of the eight required for full model fine-tuning. Despite tuning only 0.2% of LLaMA 7B's parameters, our implementation achieves better performance than the publicly-released AlpacaFarm checkpoint with full model fine-tuning. Next, we analyze several configurations of our LoRA-based PPO implementation, varying the form of the KL regularization term in the training objective. We find that (1) removing this penalty term does not harm performance on the AlpacaFarm evaluation set under our LoRA setup; (2) other regularizers, such as Jensen-Shannon divergence, lead to improved performance; and (3) while PPO training negatively impacts the factuality of model-generated responses, training with LoRA largely mitigates this effect. We release our code and pretrained checkpoints to facilitate future research on more efficient RLHF.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge