Exploring Robustness of Visual State Space model against Backdoor Attacks
Paper and Code
Aug 22, 2024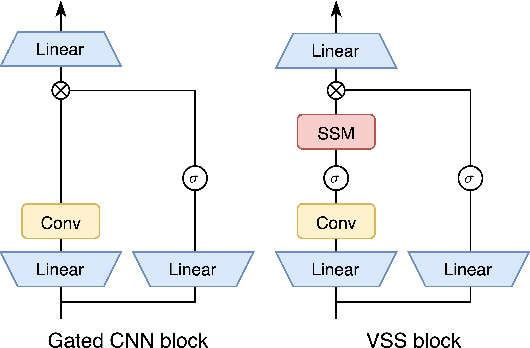
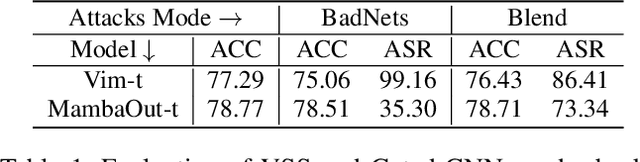

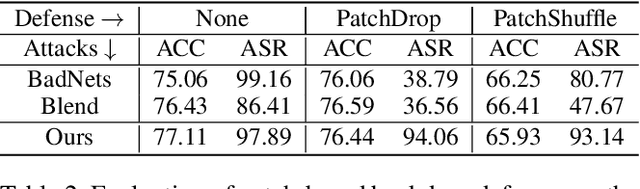
Visual State Space Model (VSS) has demonstrated remarkable performance in various computer vision tasks. However, in the process of development, backdoor attacks have brought severe challenges to security. Such attacks cause an infected model to predict target labels when a specific trigger is activated, while the model behaves normally on benign samples. In this paper, we conduct systematic experiments to comprehend on robustness of VSS through the lens of backdoor attacks, specifically how the state space model (SSM) mechanism affects robustness. We first investigate the vulnerability of VSS to different backdoor triggers and reveal that the SSM mechanism, which captures contextual information within patches, makes the VSS model more susceptible to backdoor triggers compared to models without SSM. Furthermore, we analyze the sensitivity of the VSS model to patch processing techniques and discover that these triggers are effectively disrupted. Based on these observations, we consider an effective backdoor for the VSS model that recurs in each patch to resist patch perturbations. Extensive experiments across three datasets and various backdoor attacks reveal that the VSS model performs comparably to Transformers (ViTs) but is less robust than the Gated CNNs, which comprise only stacked Gated CNN blocks without SSM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge