Exploring rhythm formant analysis for Indic language classification
Paper and Code
Oct 08, 2024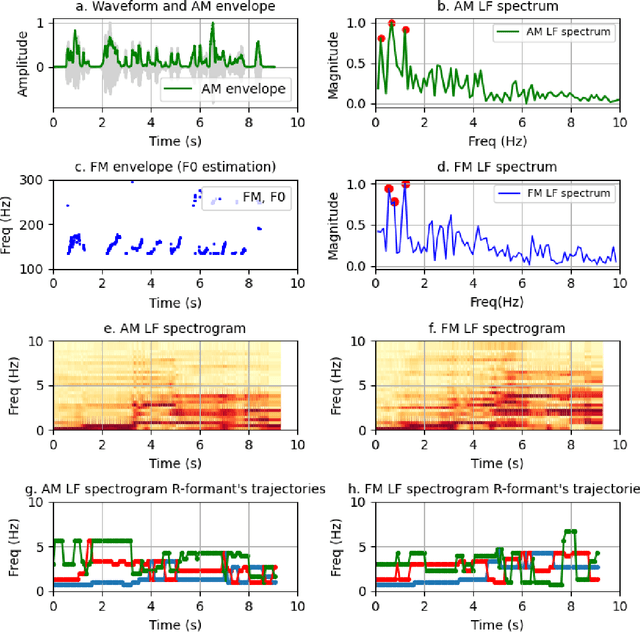
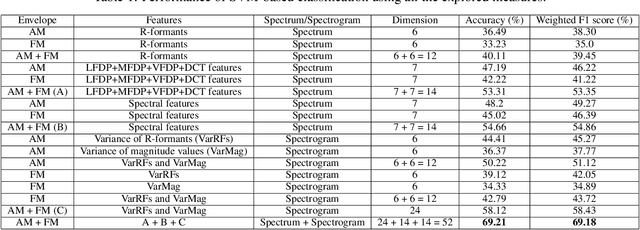
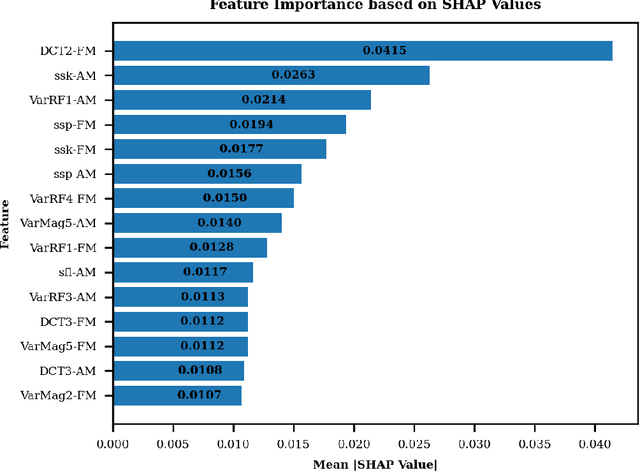
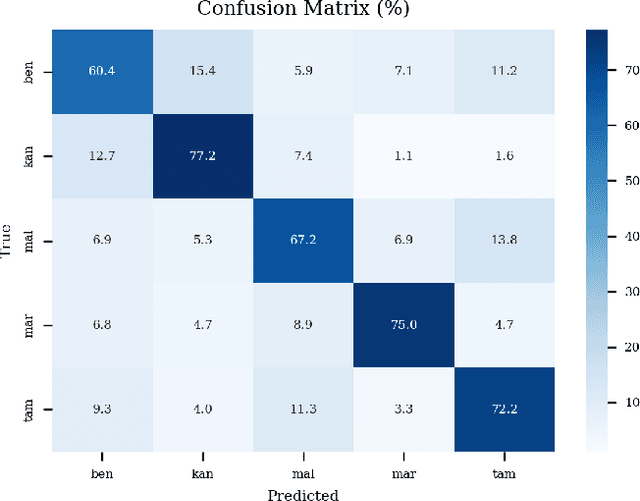
This paper reports a preliminary study on quantitative frequency domain rhythm cues for classifying five Indian languages: Bengali, Kannada, Malayalam, Marathi, and Tamil. We employ rhythm formant (R-formants) analysis, a technique introduced by Gibbon that utilizes low-frequency spectral analysis of amplitude modulation and frequency modulation envelopes to characterize speech rhythm. Various measures are computed from the LF spectrum, including R-formants, discrete cosine transform-based measures, and spectral measures. Results show that threshold-based and spectral features outperform directly computed R-formants. Temporal pattern of rhythm derived from LF spectrograms provides better language-discriminating cues. Combining all derived features we achieve an accuracy of 69.21% and a weighted F1 score of 69.18% in classifying the five languages. This study demonstrates the potential of RFA in characterizing speech rhythm for Indian language classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge