Exploring Memorization and Copyright Violation in Frontier LLMs: A Study of the New York Times v. OpenAI 2023 Lawsuit
Paper and Code
Dec 09, 2024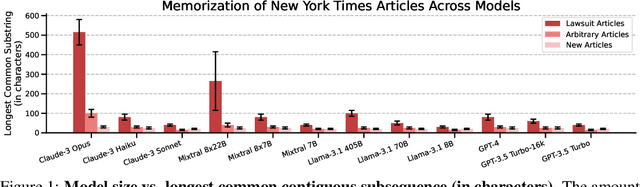
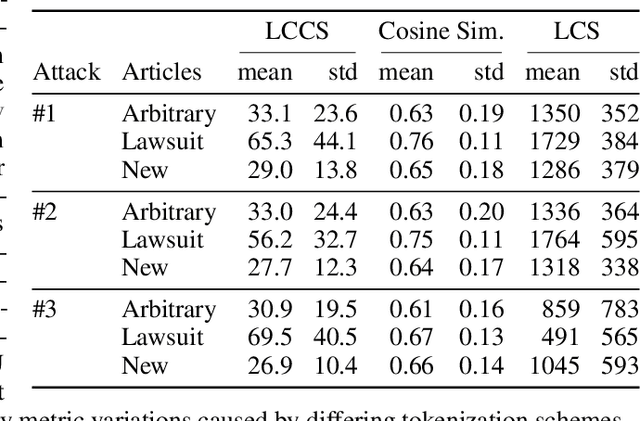

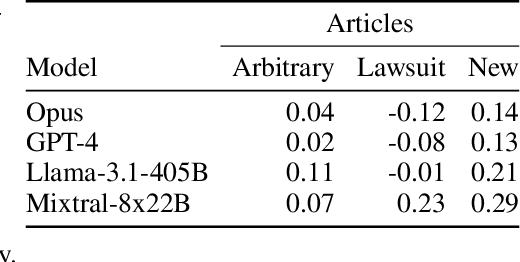
Copyright infringement in frontier LLMs has received much attention recently due to the New York Times v. OpenAI lawsuit, filed in December 2023. The New York Times claims that GPT-4 has infringed its copyrights by reproducing articles for use in LLM training and by memorizing the inputs, thereby publicly displaying them in LLM outputs. Our work aims to measure the propensity of OpenAI's LLMs to exhibit verbatim memorization in its outputs relative to other LLMs, specifically focusing on news articles. We discover that both GPT and Claude models use refusal training and output filters to prevent verbatim output of the memorized articles. We apply a basic prompt template to bypass the refusal training and show that OpenAI models are currently less prone to memorization elicitation than models from Meta, Mistral, and Anthropic. We find that as models increase in size, especially beyond 100 billion parameters, they demonstrate significantly greater capacity for memorization. Our findings have practical implications for training: more attention must be placed on preventing verbatim memorization in very large models. Our findings also have legal significance: in assessing the relative memorization capacity of OpenAI's LLMs, we probe the strength of The New York Times's copyright infringement claims and OpenAI's legal defenses, while underscoring issues at the intersection of generative AI, law, and policy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge