Exploring Long-Sequence Masked Autoencoders
Paper and Code
Oct 13, 2022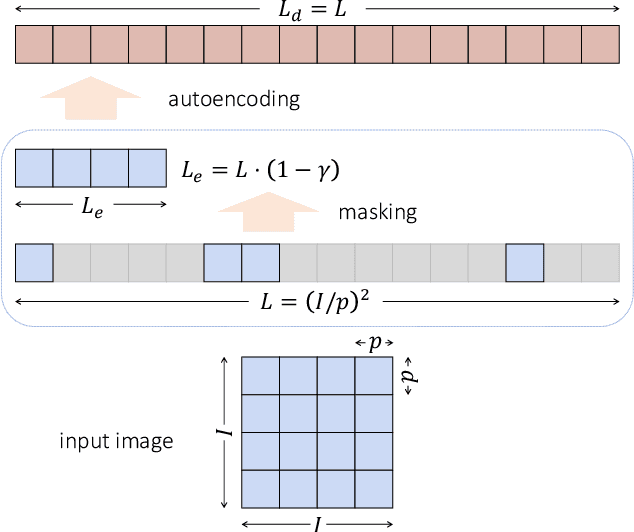

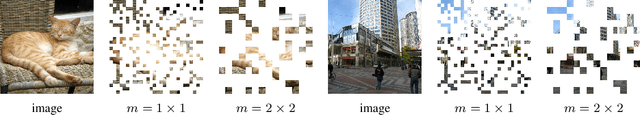

Masked Autoencoding (MAE) has emerged as an effective approach for pre-training representations across multiple domains. In contrast to discrete tokens in natural languages, the input for image MAE is continuous and subject to additional specifications. We systematically study each input specification during the pre-training stage, and find sequence length is a key axis that further scales MAE. Our study leads to a long-sequence version of MAE with minimal changes to the original recipe, by just decoupling the mask size from the patch size. For object detection and semantic segmentation, our long-sequence MAE shows consistent gains across all the experimental setups without extra computation cost during the transfer. While long-sequence pre-training is discerned most beneficial for detection and segmentation, we also achieve strong results on ImageNet-1K classification by keeping a standard image size and only increasing the sequence length. We hope our findings can provide new insights and avenues for scaling in computer vision.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge