Exploring Code Style Transfer with Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Sep 13, 2022
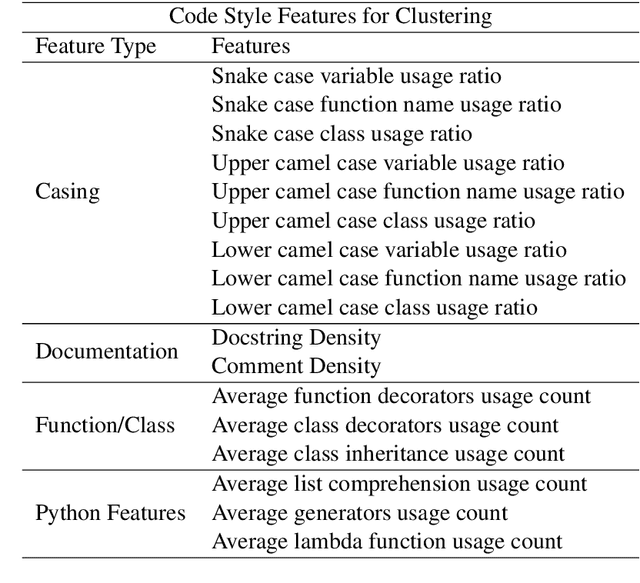
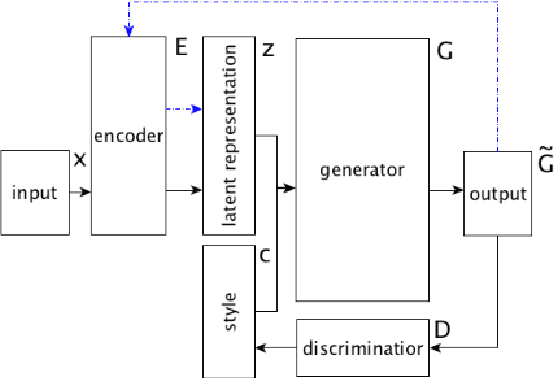

Style is a significant component of natural language text, reflecting a change in the tone of text while keeping the underlying information the same. Even though programming languages have strict syntax rules, they also have style. Code can be written with the same functionality but using different language features. However, programming style is difficult to quantify, and thus as part of this work, we define style attributes, specifically for Python. To build a definition of style, we utilized hierarchical clustering to capture a style definition without needing to specify transformations. In addition to defining style, we explore the capability of a pre-trained code language model to capture information about code style. To do this, we fine-tuned pre-trained code-language models and evaluated their performance in code style transfer tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge