Exploiting Semantics in Neural Machine Translation with Graph Convolutional Networks
Paper and Code
Apr 23, 2018
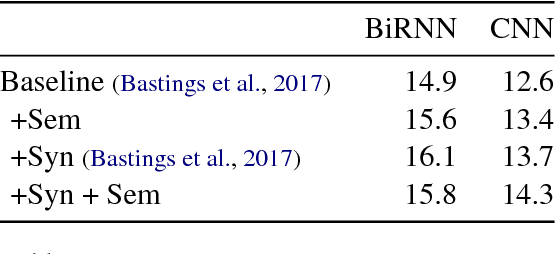
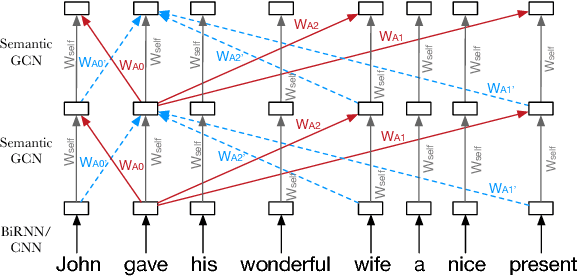

Semantic representations have long been argued as potentially useful for enforcing meaning preservation and improving generalization performance of machine translation methods. In this work, we are the first to incorporate information about predicate-argument structure of source sentences (namely, semantic-role representations) into neural machine translation. We use Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) to inject a semantic bias into sentence encoders and achieve improvements in BLEU scores over the linguistic-agnostic and syntax-aware versions on the English--German language pair.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge