Explainable Human-in-the-loop Dynamic Data-Driven Digital Twins
Paper and Code
Jul 19, 2022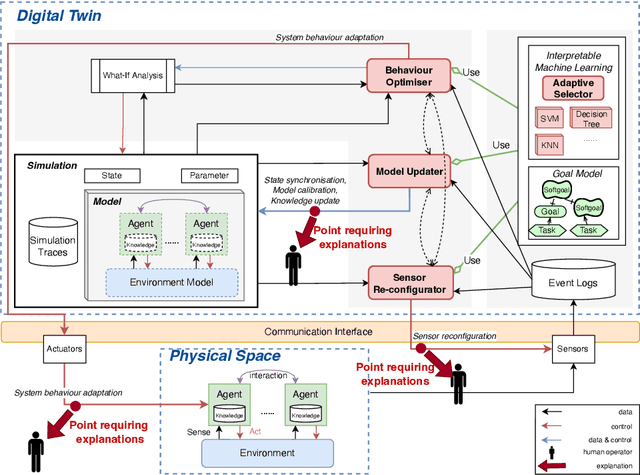
Digital Twins (DT) are essentially Dynamic Data-driven models that serve as real-time symbiotic "virtual replicas" of real-world systems. DT can leverage fundamentals of Dynamic Data-Driven Applications Systems (DDDAS) bidirectional symbiotic sensing feedback loops for its continuous updates. Sensing loops can consequently steer measurement, analysis and reconfiguration aimed at more accurate modelling and analysis in DT. The reconfiguration decisions can be autonomous or interactive, keeping human-in-the-loop. The trustworthiness of these decisions can be hindered by inadequate explainability of the rationale, and utility gained in implementing the decision for the given situation among alternatives. Additionally, different decision-making algorithms and models have varying complexity, quality and can result in different utility gained for the model. The inadequacy of explainability can limit the extent to which humans can evaluate the decisions, often leading to updates which are unfit for the given situation, erroneous, compromising the overall accuracy of the model. The novel contribution of this paper is an approach to harnessing explainability in human-in-the-loop DDDAS and DT systems, leveraging bidirectional symbiotic sensing feedback. The approach utilises interpretable machine learning and goal modelling to explainability, and considers trade-off analysis of utility gained. We use examples from smart warehousing to demonstrate the approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge