ExGAN: Adversarial Generation of Extreme Samples
Paper and Code
Sep 17, 2020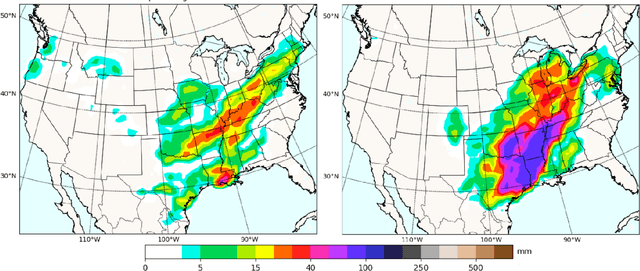

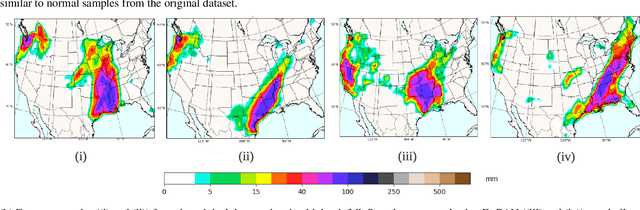
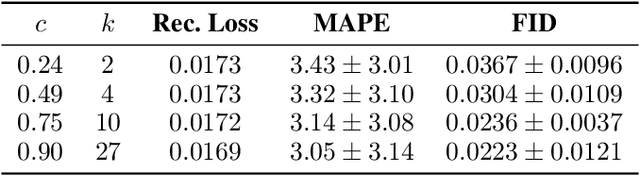
Mitigating the risk arising from extreme events is a fundamental goal with many applications, such as the modelling of natural disasters, financial crashes, epidemics, and many others. To manage this risk, a vital step is to be able to understand or generate a wide range of extreme scenarios. Existing approaches based on Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) excel at generating realistic samples, but seek to generate typical samples, rather than extreme samples. Hence, in this work, we propose ExGAN, a GAN-based approach to generate realistic and extreme samples. To model the extremes of the training distribution in a principled way, our work draws from Extreme Value Theory (EVT), a probabilistic approach for modelling the extreme tails of distributions. For practical utility, our framework allows the user to specify both the desired extremeness measure, as well as the desired extremeness probability they wish to sample at. Experiments on real US Precipitation data show that our method generates realistic samples, based on visual inspection and quantitative measures, in an efficient manner. Moreover, generating increasingly extreme examples using ExGAN can be done in constant time (with respect to the extremeness probability), as opposed to the exponential time required by the baseline approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge