Evolving Neuronal Plasticity Rules using Cartesian Genetic Programming
Paper and Code
Feb 08, 2021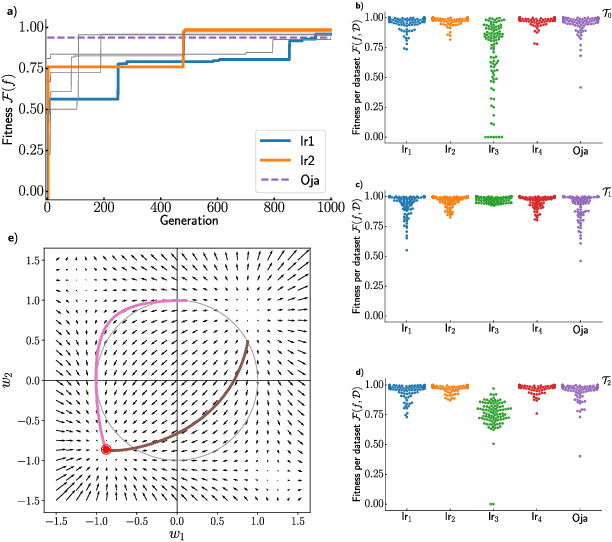
We formulate the search for phenomenological models of synaptic plasticity as an optimization problem. We employ Cartesian genetic programming to evolve biologically plausible human-interpretable plasticity rules that allow a given network to successfully solve tasks from specific task families. While our evolving-to-learn approach can be applied to various learning paradigms, here we illustrate its power by evolving plasticity rules that allow a network to efficiently determine the first principal component of its input distribution. We demonstrate that the evolved rules perform competitively with known hand-designed solutions. We explore how the statistical properties of the datasets used during the evolutionary search influences the form of the plasticity rules and discover new rules which are adapted to the structure of the corresponding datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge