Evolving Computation Graphs
Paper and Code
Jun 22, 2023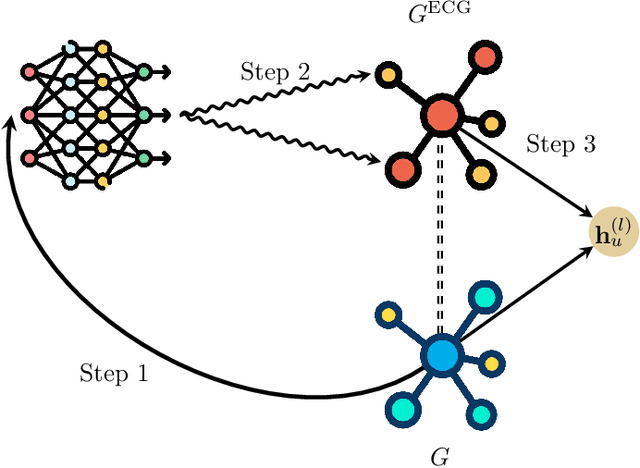
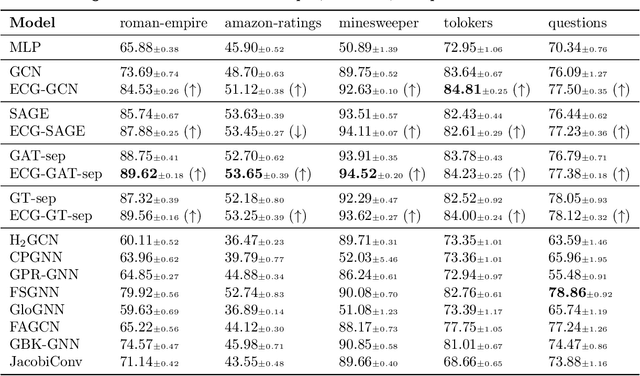
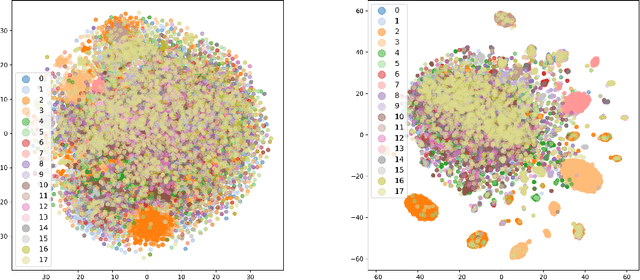
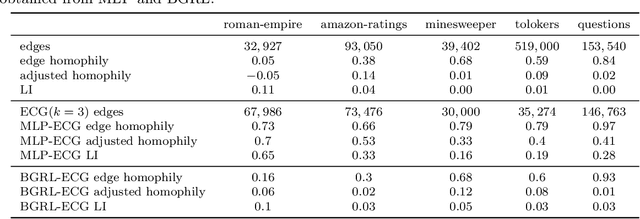
Graph neural networks (GNNs) have demonstrated success in modeling relational data, especially for data that exhibits homophily: when a connection between nodes tends to imply that they belong to the same class. However, while this assumption is true in many relevant situations, there are important real-world scenarios that violate this assumption, and this has spurred research into improving GNNs for these cases. In this work, we propose Evolving Computation Graphs (ECGs), a novel method for enhancing GNNs on heterophilic datasets. Our approach builds on prior theoretical insights linking node degree, high homophily, and inter vs intra-class embedding similarity by rewiring the GNNs' computation graph towards adding edges that connect nodes that are likely to be in the same class. We utilise weaker classifiers to identify these edges, ultimately improving GNN performance on non-homophilic data as a result. We evaluate ECGs on a diverse set of recently-proposed heterophilous datasets and demonstrate improvements over the relevant baselines. ECG presents a simple, intuitive and elegant approach for improving GNN performance on heterophilic datasets without requiring prior domain knowledge.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge